The Galloyl Group Enhances the Inhibitory Activity of Catechins against LPS-Triggered Inflammation in RAW264.7 Cells
- PMID: 39200543
- PMCID: PMC11353959
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13162616
The Galloyl Group Enhances the Inhibitory Activity of Catechins against LPS-Triggered Inflammation in RAW264.7 Cells
Abstract
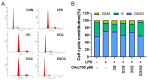
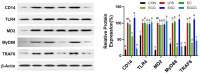
The galloyl group in catechins was confirmed to be crucial for their health benefits. However, whether the catechins' galloyl group had a contribution to their anti-inflammation remains unclear. This study investigated the anti-inflammation properties and mechanisms of catechins in RAW264.7 cells by using ELISA, fluorometry, flow cytometer, Western blot, and molecular docking. Results showed that the galloyl group enhanced the inhibitory abilities of catechins on inflammatory cytokines (NO, PGE2, IL-1β, and TNF-α) and ROS release in LPS-induced cells. This suppression was likely mediated by delaying cells from the G0/G1 to the S phase, blocking COX-2 and iNOS via the TLR4/MAPK/NF-κB pathway with PU.1 as an upstream target. The research proved that the existence of galloyl groups in catechins was indispensable for their anti-inflammatory capacities and offered a theoretical basis for the anti-inflammatory mechanism of galloylated catechins. Future research is needed to verify the anti-inflammatory effects of catechins in various sources of macrophages or the Caco-2/RAW264.7 cell co-culture system.
Keywords: TLR4/MAPK/NF-κB pathway; catechins; galloyl group; inflammation; inhibitory.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Song D., Niu J., Zhang Z., Sun Z., Wang D., Li J., Yang B., Ling N., Ji C. Purple Sweet Potato Polysaccharide Exerting an Anti-inflammatory Effect via a TLR-Mediated Pathway by Regulating Polarization and Inhibiting the Inflammasome Activation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024;72:2165–2177. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c07511. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

