Prevalence of Diamine Oxidase Enzyme (DAO) Deficiency in Subjects with Insomnia-Related Symptoms
- PMID: 39200725
- PMCID: PMC11354289
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13164583
Prevalence of Diamine Oxidase Enzyme (DAO) Deficiency in Subjects with Insomnia-Related Symptoms
Abstract
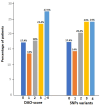
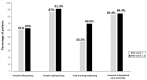
Background: To assess the prevalence of diamine oxidase (DAO) enzyme deficiency caused by single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of the AOC1 gene in a sample of patients with symptoms of insomnia. Methods: A total of 167 adult patients (>18 years of age) with symptoms of insomnia attended a specialized institute for healthy sleep, in Barcelona (Spain), between May and November 2023, and underwent genotyping analysis of the four most relevant SNP variants, including c.691G>7 (rs2052129), c.47C>T (rs10156191), c.995C>T (rs1049742), and c.1990C>G (rs1049793). Results: Genetic DAO deficiency was present in 138 patients, with a prevalence rate of 82.6% (95% CI 76-88.1%). Difficulties in staying asleep were the most common complaints in 88% of patients followed by trouble falling asleep in 60.5%. More than half of patients suffered from insomnia symptoms every day. Also, 99.4% reported daytime consequences of insomnia, with fatigue (79.6%), mood changes (72.5%), and impaired concentration in 70.1%. When patients were grouped by DAO-score, which reflected the number of heterozygous and homozygous SNPs variants, the group with a DAO-score ≥ 4 vs. 1 showed higher percentages of insomnia-related symptoms, in particular, trouble staying asleep and early morning awakening. These two symptoms were also more common in the presence of the c.1990C>G (rs1049793) variant. Conclusions: This preliminary real-world study presents novel evidence of a potential link between a DAO enzyme deficiency of a genetic origin and clinical symptoms of insomnia, which may suggest the potential benefit of DAO supplementation to improve the quality of sleep in these subjects. The study was registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT06488027).
Keywords: AOC1 gene; diamine oxidase enzyme; genetic variants; histamine; insomnia; single nucleotide polymorphism; sleep problems.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous