Surgical Navigation and CAD-CAM-Designed PEEK Prosthesis for the Surgical Treatment of Facial Intraosseous Vascular Anomalies
- PMID: 39200744
- PMCID: PMC11354805
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13164602
Surgical Navigation and CAD-CAM-Designed PEEK Prosthesis for the Surgical Treatment of Facial Intraosseous Vascular Anomalies
Abstract
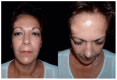
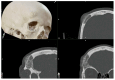
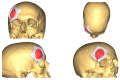
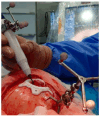
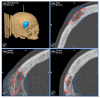
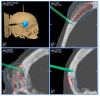
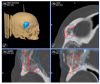
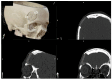
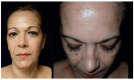
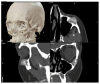
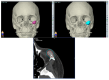
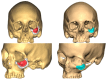
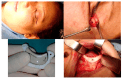
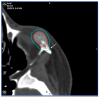
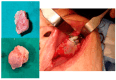
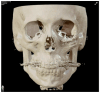
Background: Intraosseous vascular anomalies in the facial skeleton present significant diagnostic and therapeutic challenges due to complex anatomy. These anomalies represent about 0.5-1% of bony neoplastic and tumor-like lesions, usually presenting as a firm, painless mass. Most described intraosseous vascular malformations are venous malformations (VMs) and, more rarely, arteriovenous malformations. Objectives: The objectives of this work are to show our experience, protocol and the applications of computer planning, virtual surgery, CAD-CAM design, surgical navigation, and computer-assisted navigated piezoelectric surgery in the treatment of facial intraosseous vascular anomalies and to evaluate the advantages and disadvantages. Methods: Three females and one male with periorbital intraosseous vascular anomalies were treated using en-block resection and immediate reconstruction with a custom-made PEEK prosthesis. One lesion was in the supraorbital rim and orbital roof, one in the frontal bone and orbital roof, and two in the zygomatic region. We accomplished the resection and reconstruction of the lesion using virtual planning, CAD-CAM design, surgical navigation and piezoelectric device navigation. Results: There were no complications related to the surgery assisted with navigation. With an accuracy of less than 1 mm, the procedure may be carried out in accordance with the surgical plan. The surgeon's degree of uncertainty during deep osteotomies and in locations with low visibility was decreased by the use of the navigated piezoelectric device. Conclusions: Resection and reconstruction of facial intraosseous vascular anomalies benefit from this new surgical strategy using CAD-CAM technologies, computer-assisted navigated piezoelectric surgery, and surgical navigation.
Keywords: 3D planning; CAD-CAM design; computed-assisted surgery; computer-assisted navigated piezoelectric surgery; surgical navigation; virtual planning; virtual surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Wassef M., Blei F., Adams D., Alomari A., Baselga E., Berestein A., Burrows P., Frieden I.J., Garzon M.C., Lopez-Gutierrez J.C., et al. Vascular anomalies classification: Recommendations from the international society for the study of vascular anomalies. Pediatrics. 2015;136:e203–e214. doi: 10.1542/peds.2014-3673. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

