Evaluation of Peri-Implantitis Bone Defect Healing: Comparing the Efficacy of Small-Particle Dentin and Bio-Oss in Bone Density Attenuation
- PMID: 39200780
- PMCID: PMC11354878
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13164638
Evaluation of Peri-Implantitis Bone Defect Healing: Comparing the Efficacy of Small-Particle Dentin and Bio-Oss in Bone Density Attenuation
Abstract
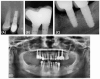
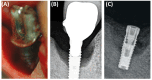
Introduction: Peri-implantitis is a serious complication in dental implantology that, if left untreated, may lead to implant loss and systemic diseases. Effective regeneration of bone defects resulting from peri-implantitis is crucial to maintaining the functionality of dental implants. Purpose of the Study: The study aimed to compare the effectiveness of fine-particle dentin and Bio-Oss in the reconstruction of bone defects caused by peri-implantitis. Materials and Methods: The study included a comprehensive radiological assessment of changes in bone density over time. Bone density was assessed using Hounsfield Units (HUs) as a measure of bone attenuation, with radiological assessments performed at 8- and 12-week intervals during the healing process. The study included participants ranging in age from 30 to 65 years. Fifty-seven patients were divided into three groups: 22 patients received small-particle dentin, 15 received Bio-Oss, and 20 controls without bone substitute material. Results: The fine-dentin group showed a 20% increase in bone density after 8 weeks (p < 0.05), while the Bio-Oss group showed a 15% increase after 12 weeks (p < 0.05). The control group showed minimal changes in bone density (5% after 12 weeks), which was not statistically significant. Clinical evaluations showed 95% successful integration in the fine dentin group, 85% in the Bio-Oss group, and 70% in the control group. The fine-dentin group showed a 20% increase in bone density after 8 weeks (p < 0.05), while the Bio-Oss group showed a 15% increase after 12 weeks (p < 0.05). The control group showed minimal changes in bone density (5% after 12 weeks), which was not statistically significant. Clinical evaluations showed 95% successful integration in the fine-dentin group, 85% in the Bio-Oss group, and 70% in the control group. Conclusions: Both fine-particle dentin and Bio-Oss significantly improved bone density compared to the control group. Fine-particle dentin is suitable for immediate bone regeneration due to its rapid initial regeneration, while Bio-Oss provides long-term support, ideal for maintaining implant stability over a longer period of time. The results highlight the importance of selecting appropriate bone replacement materials depending on the clinical scenario to improve patient outcomes after dental implant placement.
Keywords: Bio-Oss; bone regeneration; bone substitute materials; periimplantitis; small-particle dentin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Jepsen S., Schwarz F., Cordaro L., Derks J., Hämmerle C.H.F., Heitz-Mayfield L.J., Hernández-Alfaro F., Meijer H.J.A., Naenni N., Ortiz-Vigón A., et al. Regeneration of alveolar ridge defects. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2019;46:S82–S91. - PubMed
-
- Saska S., Mendes L.S., Gaspar A.M.M., Sidorenko de Oliveira Capote T. Bone Substitutes. IntechOpen; London, UK: 2015. Bone Substitute Materials in Implant Dentistry; pp. 1–20.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

