Retinitis Pigmentosa and Therapeutic Approaches: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 39200821
- PMCID: PMC11355744
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13164680
Retinitis Pigmentosa and Therapeutic Approaches: A Systematic Review
Abstract
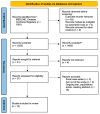
Background: Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is a group of hereditary retinal dystrophies characterized by progressive degeneration of photoreceptor cells, which results in debilitating visual impairment. This systematic review aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of emerging treatment modalities for RP, including gene therapy, mesenchymal-cell-based approaches, and supplementary interventions. Methods: A comprehensive search of electronic databases was conducted to identify relevant studies published up to February 2024. Studies reporting outcomes of treatment interventions for RP, including randomized controlled trials, non-randomized studies, and case series, were included. Data extraction and synthesis were performed according to predefined criteria, focusing on assessing the quality of evidence and summarizing key findings. Results: The search yielded 13 studies meeting inclusion criteria, encompassing diverse treatment modalities and study designs. Gene therapy emerged as a promising therapeutic approach, with several studies reporting favorable outcomes regarding visual function preservation and disease stabilization. Mesenchymal-cell-based therapies also demonstrated potential benefits, although evidence remains limited and heterogeneous. Supplementary interventions, including nutritional supplements and neuroprotective agents, exhibited variable efficacy, with conflicting findings across studies. Conclusions: Despite the lack of definitive curative treatments, emerging therapeutic modalities promise to slow disease progression and preserve visual function in individuals with RP. However, substantial gaps in evidence and heterogeneity in study methodologies underscore the need for further research to elucidate optimal treatment strategies, refine patient selection criteria, and enhance long-term outcomes. This systematic review provides a comprehensive synthesis of current evidence and highlights directions for future research to advance the care and management of individuals with RP.
Keywords: gene therapy; inherited retinal dystrophy; retinal disease; retinitis pigmentosa.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

