Long COVID Syndrome: A Narrative Review on Burden of Age and Vaccination
- PMID: 39200898
- PMCID: PMC11355827
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13164756
Long COVID Syndrome: A Narrative Review on Burden of Age and Vaccination
Abstract
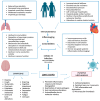
Background/Objective: The COVID-19 pandemic has led to the emergence of post-acute COVID-19 syndrome, also known as long COVID, which presents a significant challenge due to its varied symptoms and unpredictable course, particularly in older adults. Similar to COVID-19 infections, factors such as age, pre-existing health conditions, and vaccination status may influence the occurrence and severity of long COVID. The objective is to analyze the role of aging in the context of long COVID and to investigate prevalence rates and vaccination efficacy to improve prevention strategies and treatment in this age group. Methods: Four researchers independently conducted a literature search of the PubMed database to trace studies published between July 2020 and July 2024. Results: Aging influences both the likelihood of developing long COVID and the recovery process, due to age-related physiological changes, immune system alterations, and the presence of comorbidities. Vaccination plays a key role in reducing the risk of long COVID by attenuating the inflammatory responses associated with its symptoms. Conclusions: Despite the protection vaccines offer against severe infection, hospitalization, and post-infection sequelae, vaccine hesitancy remains a major obstacle, worsening the impact of long COVID. Promising treatments for this condition include antivirals although further research is needed.
Keywords: COVID-19; aging; long COVID; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- COVID-19 Deaths|WHO COVID-19 Dashboard. Datadot. [(accessed on 5 February 2024)]. Available online: https://data.who.int/dashboards/COVID19/cases.
-
- Soriano J.B., Murthy S., Marshall J.C., Relan P., Diaz J.V., WHO Clinical Case Definition Working Group on Post-COVID-19 Condition A clinical case definition of post-COVID-19 condition by a Delphi consensus. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022;22:e102–e107. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00703-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fernández-de-Las-Peñas C., Palacios-Ceña D., Gómez-Mayordomo V., Florencio L.L., Cuadrado M.L., Plaza-Manzano G., Navarro-Santana M. Prevalence of post-COVID-19 symptoms in hospitalized and non-hospitalized COVID-19 survivors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2021;92:55–70. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2021.06.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources