Diabetes Management Based on the Phenotype and Stage of the Disease: An Expert Proposal from the AGORA Diabetes Collaborative Group
- PMID: 39200982
- PMCID: PMC11355114
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13164839
Diabetes Management Based on the Phenotype and Stage of the Disease: An Expert Proposal from the AGORA Diabetes Collaborative Group
Abstract
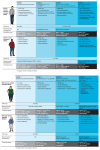
Diabetes is a complex and rapidly growing disease with heterogeneous clinical presentations. Recent advances in molecular and genetic technologies have led to the identification of various subtypes of diabetes. These advancements offer the potential for a more precise, individualized approach to treatment, known as precision medicine. Recognizing high-risk phenotypes and intervening early and intensively is crucial. A staging system for type 1 diabetes has been proposed and accepted globally. In this article, we will explore the different methods for categorizing and classifying type 2 diabetes (T2D) based on clinical characteristics, progression patterns, risk of complications, and the use of molecular techniques for patient grouping. We, as a team of experts, will also present an easy-to-follow treatment plan and guidance for non-specialists, particularly primary care physicians, that integrates the classification and staging of diabetes. This will help ensure that the most suitable therapy is applied to the different types of T2D at each stage of the disease's progression.
Keywords: diabetes; diabetes complications; diabetes/disease-modifying drugs; insulin deficiency; insulin resistance; precision medicine; staging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ahlqvist E., Storm P., Käräjämäki A., Martinell M., Dorkhan M., Carlsson A., Vikman P., Prasad R.B., Aly D.M., Almgren P., et al. Novel Subgroups of Adult-Onset Diabetes and Their Association with Outcomes: A Data-Driven Cluster Analysis of Six Variables. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6:361–369. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30051-2. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

