Enhancing Parental Understanding of Emotions in Children with Developmental Language Disorder: An Online Parent-Led Intervention Program
- PMID: 39201130
- PMCID: PMC11354076
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare12161571
Enhancing Parental Understanding of Emotions in Children with Developmental Language Disorder: An Online Parent-Led Intervention Program
Abstract
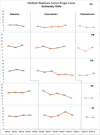
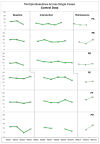
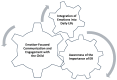
Many children with developmental language disorder (DLD) have emotion recognition and regulation difficulties, but there are currently no known interventions enhancing emotional awareness in this population. This study explores the impact of parents' perspectives regarding children with DLD emotional understanding through a parent-led online emotion recognition (ER) intervention. Ten parents of children with DLD aged 6-11 participated in the study. A nonconcurrent multiple baseline design was employed, allowing for a rigorous analysis of changes in parental beliefs over time. Weekly data were collected through the Parents' Beliefs About Children's Emotions Questionnaire. Interviews were also conducted to gain deeper insights into parents' perceptions regarding the ER skills of their children. Results indicated that parents' beliefs about the need for guiding and supporting their child's ER skills increased over the intervention. Interviews also supported this, and three main themes were generated. The intervention program increased parents' awareness of (a) the importance of ER for children with DLD, (b) emotion-focused communication and engagement with their child, and (c) the integration of emotions into daily life. This study is the first known study that explores parents' beliefs about children with DLD ER skills, highlighting the importance of supporting parents through accessible interventions.
Keywords: developmental language disorder; emotion recognition; intervention; parent-led.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A randomized study of parent- versus child-directed intervention for Dutch toddlers with DLD.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2023 Sep-Oct;58(5):1768-1782. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12901. Epub 2023 May 29. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2023. PMID: 37248804 Clinical Trial.
-
Vocabulary Abilities and Parents' Emotional Regulation Predict Emotional Regulation in School-Age Children but Not Adolescents With and Without Developmental Language Disorder.Front Psychol. 2021 Dec 9;12:748283. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.748283. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34955966 Free PMC article.
-
Supporting the mental health of children with speech, language and communication needs: The views and experiences of parents.Autism Dev Lang Impair. 2022 May 29;7:23969415221101137. doi: 10.1177/23969415221101137. eCollection 2022 Jan-Dec. Autism Dev Lang Impair. 2022. PMID: 36124076 Free PMC article.
-
Parental emotion and emotion regulation: A critical target of study for research and intervention to promote child emotion socialization.Dev Psychol. 2020 Mar;56(3):403-417. doi: 10.1037/dev0000864. Dev Psychol. 2020. PMID: 32077713 Review.
-
Efficacy, model of delivery, intensity and targets of pragmatic interventions for children with developmental language disorder: A systematic review.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2022 Jul;57(4):764-781. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12716. Epub 2022 Apr 20. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2022. PMID: 35445482 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

