Impact of Skin Exposure to Benzo[a]pyrene in Rat Model: Insights into Epidermal Cell Function and Draining Lymph Node Cell Response
- PMID: 39201318
- PMCID: PMC11354278
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25168631
Impact of Skin Exposure to Benzo[a]pyrene in Rat Model: Insights into Epidermal Cell Function and Draining Lymph Node Cell Response
Abstract
The skin is a direct target of the air pollutant benzo[a]pyrene (BaP). While its carcinogenic qualities are well-studied, the immunotoxicity of BaP after dermal exposure is less understood. This study examines the immunomodulatory effects of a 10-day epicutaneous BaP application, in environmentally/occupationally relevant doses, by analyzing ex vivo skin immune response (skin explant, epidermal cells and draining lymph node/DLN cell activity), alongside the skin's reaction to sensitization with experimental hapten dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB). The results show that BaP application disrupts the structure of the epidermal layer and promotes immune cell infiltration in the dermis. BaP exposure led to oxidative stress in epidermal cells, characterized by decreased reduced glutathione and increased AHR and Cyp1A1 expression. Production and gene expression of proinflammatory cytokines (TNF, IL-1β) by epidermal cells decreased, while IL-10 response increased. Decreased spontaneous production of IFN-γ and IL-17, along with unchanged IL-10, was observed in DLC cells, whereas ConA-stimulated production of these cytokines was elevated. Local immunosuppression caused by BaP application seems to reduce the skin's response to an additional stimulus, evidenced by decreased effector activity of DLN cells three days after sensitization with DNCB. These findings provide new insight into the immunomodulatory effects and health risks associated with skin exposure to BaP.
Keywords: draining lymph nodes cell activity; epicutaenous benzo[a]pyrene application; epidermal cell activity; rats; skin explants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
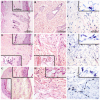
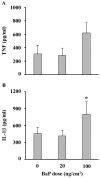


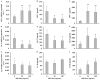
References
-
- Luo K., Stepanov I., Hecht S.S. Chemical biomarkers of exposure and early damage from potentially carcinogenic airborne pollutants. Ann. Cancer Epidemiol. 2019;3:5. doi: 10.21037/ace.2019.08.01. - DOI
-
- Bourgart E., Persoons R., Marques M., Rivier A., Balducci F., von Koschembahr A., Beal D., Leccia M.-T., Douki T., Maitre A. Influence of exposure dose, complex mixture, and ultraviolet radiation on skin absorption and bioactivation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons ex vivo. Arch. Toxicol. 2019;93:2165–2184. doi: 10.1007/s00204-019-02504-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Finardi S., Radice P., Cecinato A., Gariazzo C., Gherardi M., Romagnoli P. Seasonal variation of PAHs concentration and source attribution through diagnostic ratios analysis. Urban Clim. 2017;22:19–34. doi: 10.1016/j.uclim.2015.12.001. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

