Lactoferrin Affects the Viability of Bacteria in a Biofilm and the Formation of a New Biofilm Cycle of Mannheimia haemolytica A2
- PMID: 39201405
- PMCID: PMC11355051
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25168718
Lactoferrin Affects the Viability of Bacteria in a Biofilm and the Formation of a New Biofilm Cycle of Mannheimia haemolytica A2
Abstract
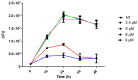
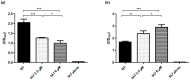
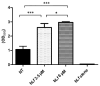
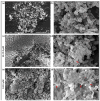
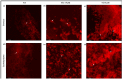
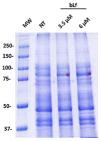
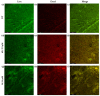
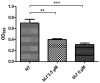
Respiratory diseases in ruminants are responsible for enormous economic losses for the dairy and meat industry. The main causative bacterial agent of pneumonia in ovine is Mannheimia haemolytica A2. Due to the impact of this disease, the effect of the antimicrobial protein, bovine lactoferrin (bLf), against virulence factors of this bacterium has been studied. However, its effect on biofilm formation has not been reported. In this work, we evaluated the effect on different stages of the biofilm. Our results reveal a decrease in biofilm formation when bacteria were pre-incubated with bLf. However, when bLf was added at the start of biofilm formation and on mature biofilm, an increase was observed, which was visualized by greater bacterial aggregation and secretion of biofilm matrix components. Additionally, through SDS-PAGE, a remarkable band of ~80 kDa was observed when bLf was added to biofilms. Therefore, the presence of bLf on the biofilm was determined through the Western blot and Microscopy techniques. Finally, by using Live/Dead staining, we observed that most of the bacteria in a biofilm with bLf were not viable. In addition, bLf affects the formation of a new biofilm cycle. In conclusion, bLf binds to the biofilm of M. haemolytica A2 and affects the viability of bacteria and the formation a new biofilm cycle.
Keywords: Mannheimia haemolytica; biofilm; bovine Lactoferrin; confocal laser microscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abdulkadir M., Nigussie T., Kebede I.A. Isolation and Identification of Pasteurella multocida and Mannheimia haemolytica from Pneumonic Small Ruminants and Their Antibiotic Susceptibility in Haramaya District, Eastern Ethiopia. Sci. World J. 2024;2024:5605552. doi: 10.1155/2024/5605552. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

