Uncovering the Expression Pattern of the Costimulatory Receptors ICOS, 4-1BB, and OX-40 in Exhausted Peripheral and Tumor-Infiltrating Natural Killer Cells from Patients with Cervical Cancer
- PMID: 39201462
- PMCID: PMC11354483
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25168775
Uncovering the Expression Pattern of the Costimulatory Receptors ICOS, 4-1BB, and OX-40 in Exhausted Peripheral and Tumor-Infiltrating Natural Killer Cells from Patients with Cervical Cancer
Abstract
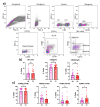
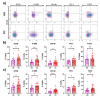
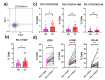
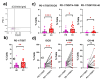
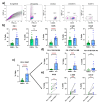
Cervical cancer (CC) poses a significant health burden, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. NK cells play a crucial role against CC; however, they can become exhausted and lose their cytotoxic capacity. This work explores the expression of costimulatory receptors (ICOS, 4-1BB, OX-40) in exhausted NK cells from CC patients. Peripheral blood and tumor biopsies were collected, and flow cytometry was used to evaluate the expression of costimulatory receptors in exhausted NK cells. There is an increase of peripheral exhausted NK cells (PD-1+TIGIT+) in CC patients; this subpopulation has a selectively increased expression of the costimulatory receptors ICOS and 4-1BB. An exhausted population is also highly increased in tumor-infiltrating NK cells, and it shows a dramatically increased expression of the costimulatory receptors ICOS (>15×) and 4-1BB (>10×) compared to peripheral NK cells. The exhausted cells, both in the periphery and in the tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), are also more likely than non-exhausted NK cell populations (PD-1-TIGIT-) to express these costimulatory receptors; increases ranging from 2.0× ICOS, 2.4× 4-1BB, and 2.6× OX-40 in CD56dim PBMCs to 1.5× ICOS, 5× 4-1BB, and 10× OX-40 in TILs were found. Our study demonstrates for the first time the increased expression of the costimulatory receptors ICOS, 4-1BB, and OX-40 in peripheral CD56dim, CD56bright, and tumor-infiltrating NK cells in CC. Targeting these receptors for stimulation could reverse exhaustion and be a promising immunotherapy strategy.
Keywords: 4-1BB; ICOS; NK cells; OX-40; PD-1; TIGIT; cervical cancer; exhaustion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beyond Canonical Immune Checkpoints: Overexpression of TNFRSF Members 4-1BB and OX-40 Marks T Cells Exhibiting Phenotypic Features of Exhaustion in Cervical Carcinoma.Immunology. 2025 Aug;175(4):482-500. doi: 10.1111/imm.13945. Epub 2025 May 19. Immunology. 2025. PMID: 40387515
-
4-1BB Delineates Distinct Activation Status of Exhausted Tumor-Infiltrating CD8+ T Cells in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Hepatology. 2020 Mar;71(3):955-971. doi: 10.1002/hep.30881. Epub 2019 Oct 18. Hepatology. 2020. PMID: 31353502 Free PMC article.
-
Immune checkpoint expression on peripheral cytotoxic lymphocytes in cervical cancer patients: moving beyond the PD-1/PD-L1 axis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2021 Apr;204(1):78-95. doi: 10.1111/cei.13561. Epub 2021 Jan 18. Clin Exp Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33306195 Free PMC article.
-
Role of chemokines in the biology of natural killer cells.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010;341:37-58. doi: 10.1007/82_2010_20. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20369317 Review.
-
Immunotherapy targeting 4-1BB: mechanistic rationale, clinical results, and future strategies.Blood. 2018 Jan 4;131(1):49-57. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-06-741041. Epub 2017 Nov 8. Blood. 2018. PMID: 29118009 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

