Clinical Significance of B-Type Natriuretic Peptide and N-Terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide in Pediatric Patients: Insights into Their Utility in the Presence or Absence of Pre-Existing Heart Conditions
- PMID: 39201467
- PMCID: PMC11354905
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25168781
Clinical Significance of B-Type Natriuretic Peptide and N-Terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide in Pediatric Patients: Insights into Their Utility in the Presence or Absence of Pre-Existing Heart Conditions
Abstract
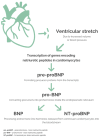
The clinical significance of B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) in pediatric patients remains an area of evolving understanding, particularly regarding their utility in the presence or absence of pre-existing heart conditions. While clear cutoff values and established roles in heart failure are understood in adult patients, pediatric norms vary with age, complicating interpretation. Notably, the emergence of multi-system inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) has highlighted the importance of these markers not only in the detection of acute heart failure but also as a marker of disease severity and even as a differential diagnosis tool. This review summarizes current knowledge on the utility of BNP and NT-proBNP in pediatric patients. Their unique physiology, including circulation and compensation mechanisms, likely influence BNP and NT-proBNP release, potentially even in non-heart failure states. Factors such as dynamic volemic changes accompanying inflammatory diseases in children may contribute. Thus, understanding the nuanced roles of BNP and NT-proBNP in pediatric populations is crucial for the accurate diagnosis, management, and differentiation of cardiac and non-cardiac conditions.
Keywords: BNP; Kawasaki disease; MIS-C; children; heart failure.
Conflict of interest statement
K.M.L., B.P., and L.S. are employees of Wroclaw Medical University. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Mueller C., McDonald K., de Boer R.A., Maisel A., Cleland J.G.F., Kozhuharov N., Coats A.J.S., Metra M., Mebazaa A., Ruschitzka F., et al. Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology practical guidance on the use of natriuretic peptide concentrations. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2019;21:715–731. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1494. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials