Is Exon Skipping a Viable Therapeutic Approach for Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome with Mutations in COL3A1 Exon 10 or 15?
- PMID: 39201504
- PMCID: PMC11354334
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25168816
Is Exon Skipping a Viable Therapeutic Approach for Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome with Mutations in COL3A1 Exon 10 or 15?
Abstract
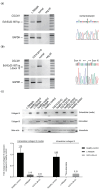
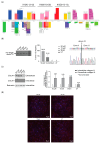
Vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome or Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV (vEDS) is a connective tissue disorder characterised by skin hyperextensibility, joint hypermobility and fatal vascular rupture caused by COL3A1 mutations that affect collagen III expression, homo-trimer assembly and secretion. Along with collagens I, II, V and XI, collagen III plays an important role in the extracellular matrix, particularly in the inner organs. To date, only symptomatic treatment for vEDS patients is available. Fibroblasts derived from vEDS patients carrying dominant negative and/or haploinsufficiency mutations in COL3A1 deposit reduced collagen III in the extracellular matrix. This study explored the potential of an antisense oligonucleotide (ASO)-mediated splice modulating strategy to bypass disease-causing COL3A1 mutations reported in the in-frame exons 10 and 15. Antisense oligonucleotides designed to redirect COL3A1 pre-mRNA processing and excise exons 10 or 15 were transfected into dermal fibroblasts derived from vEDS patients and a healthy control subject. Efficient exon 10 or 15 excision from the mature COL3A1 mRNA was achieved and intracellular collagen III expression was increased after treatment with ASOs; however, collagen III deposition into the extracellular matrix was reduced in patient cells. The region encoded by exon 10 includes a glycosylation site, and exon 15 encodes hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine-containing triplet repeats, predicted to be crucial for collagen III assembly. These results emphasize the importance of post-translational modification for collagen III homo-trimer assembly. In conclusion, while efficient skipping of target COL3A1 exons was achieved, the induced collagen III isoforms generated showed defects in extracellular matrix formation. While therapeutic ASO-mediated exon skipping is not indicated for the patients in this study, the observations are restricted to exons 10 and 15 and may not be applicable to other collagen III in-frame exons.
Keywords: COL3A1; Vascular Ehler-Danlos Syndrome; antisense oligonucleotides; collagen III.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Transcriptome analysis of skin fibroblasts with dominant negative COL3A1 mutations provides molecular insights into the etiopathology of vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.PLoS One. 2018 Jan 18;13(1):e0191220. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191220. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29346445 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal type III collagen produced by an exon-17-skipping mutation of the COL3A1 gene in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV is not incorporated into the extracellular matrix.Biochem J. 1995 Nov 1;311 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):939-43. doi: 10.1042/bj3110939. Biochem J. 1995. PMID: 7487954 Free PMC article.
-
Patient-derived extracellular matrix demonstrates role of COL3A1 in blood vessel mechanics.Acta Biomater. 2023 Aug;166:346-359. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.05.015. Epub 2023 May 13. Acta Biomater. 2023. PMID: 37187299 Free PMC article.
-
Type III collagen (COL3A1): Gene and protein structure, tissue distribution, and associated diseases.Gene. 2019 Jul 30;707:151-171. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.05.003. Epub 2019 May 7. Gene. 2019. PMID: 31075413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Frameshift COL3A1 Variant in Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome.Ann Vasc Surg. 2019 Nov;61:472.e9-472.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2019.05.057. Epub 2019 Aug 5. Ann Vasc Surg. 2019. PMID: 31394236 Review.
References
-
- Boot-Handford R.P., Tuckwell D.S., Plumb D.A., Rock C.F., Poulsom R. A novel and highly conserved collagen (pro(alpha)1(XXVII)) with a unique expression pattern and unusual molecular characteristics establishes a new clade within the vertebrate fibrillar collagen family. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:31067–31077. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M212889200. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Koch M., Laub F., Zhou P., Hahn R.A., Tanaka S., Burgeson R.E., Gerecke D.R., Ramirez F., Gordon M.K. Collagen XXIV, a vertebrate fibrillar collagen with structural features of invertebrate collagens: Selective expression in developing cornea and bone. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:43236–43244. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M302112200. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

