Role of PRMT1 and PRMT5 in Breast Cancer
- PMID: 39201539
- PMCID: PMC11354362
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25168854
Role of PRMT1 and PRMT5 in Breast Cancer
Abstract
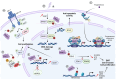
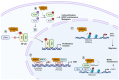
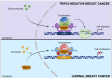
Breast cancer is the most common cancer diagnosed in women worldwide. Early-stage breast cancer is curable in ~70-80% of patients, while advanced metastatic breast cancer is considered incurable with current therapies. Breast cancer is a highly heterogeneous disease categorized into three main subtypes based on key markers orientating specific treatment strategies for each subtype. The complexity of breast carcinogenesis is often associated with epigenetic modification regulating different signaling pathways, involved in breast tumor initiation and progression, particularly by the methylation of arginine residues. Protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMT1-9) have emerged, through their ability to methylate histones and non-histone substrates, as essential regulators of cancers. Here, we present an updated overview of the mechanisms by which PRMT1 and PRMT5, two major members of the PRMT family, control important signaling pathways impacting breast tumorigenesis, highlighting them as putative therapeutic targets.
Keywords: PRMT1; PRMT5; arginine methylation; breast cancer; cell signaling; transcriptional regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Methylation of C/EBPα by PRMT1 Inhibits Its Tumor-Suppressive Function in Breast Cancer.Cancer Res. 2019 Jun 1;79(11):2865-2877. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-3211. Epub 2019 Apr 23. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31015230
-
Hypoxia-induced PRMT1 methylates HIF2β to promote breast tumorigenesis via enhancing glycolytic gene transcription.Cell Rep. 2025 Apr 22;44(4):115487. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115487. Epub 2025 Apr 1. Cell Rep. 2025. PMID: 40173041
-
The dual function of PRMT1 in modulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cellular senescence in breast cancer cells through regulation of ZEB1.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 27;6:19874. doi: 10.1038/srep19874. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26813495 Free PMC article.
-
PRMT1 in human neoplasm: cancer biology and potential therapeutic target.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Feb 8;22(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01506-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38326807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic arginine methylation in breast cancer: emerging therapeutic strategies.J Mol Endocrinol. 2019 Apr 1;62(3):R223-R237. doi: 10.1530/JME-18-0224. J Mol Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 30620710 Review.
Cited by
-
Prmt1-mediated methylation regulates Ncoa4 stability to transactivate Adamts genes and promote bone extracellular matrix degradation in chronic hematogenous osteomyelitis.Biol Direct. 2025 May 9;20(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13062-025-00652-9. Biol Direct. 2025. PMID: 40346625 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic targeting of protein arginine methyltransferases reduces breast cancer progression by disrupting angiogenic pathways.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025 Jul 31;43:102172. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2025.102172. eCollection 2025 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025. PMID: 40791817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions and mechanisms of non-histone post-translational modifications in cancer progression.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Mar 31;11(1):125. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02410-2. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40164592 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

