Nucleic Acid Armor: Fortifying RNA Therapeutics through Delivery and Targeting Innovations for Immunotherapy
- PMID: 39201574
- PMCID: PMC11354913
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25168888
Nucleic Acid Armor: Fortifying RNA Therapeutics through Delivery and Targeting Innovations for Immunotherapy
Abstract
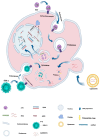
RNA is a promising nucleic acid-based biomolecule for various treatments because of its high efficacy, low toxicity, and the tremendous availability of targeting sequences. Nevertheless, RNA shows instability and has a short half-life in physiological environments such as the bloodstream in the presence of RNAase. Therefore, developing reliable delivery strategies is important for targeting disease sites and maximizing the therapeutic effect of RNA drugs, particularly in the field of immunotherapy. In this mini-review, we highlight two major approaches: (1) delivery vehicles and (2) chemical modifications. Recent advances in delivery vehicles employ nanotechnologies such as lipid-based nanoparticles, viral vectors, and inorganic nanocarriers to precisely target specific cell types to facilitate RNA cellular entry. On the other hand, chemical modification utilizes the alteration of RNA structures via the addition of covalent bonds such as N-acetylgalactosamine or antibodies (antibody-oligonucleotide conjugates) to target specific receptors of cells. The pros and cons of these technologies are enlisted in this review. We aim to review nucleic acid drugs, their delivery systems, targeting strategies, and related chemical modifications. Finally, we express our perspective on the potential combination of RNA-based click chemistry with adoptive cell therapy (e.g., B cells or T cells) to address the issues of short duration and short half-life associated with antibody-oligonucleotide conjugate drugs.
Keywords: RNA drugs; antibody–oligonucleotide conjugates; immunotherapy; nanotechnology; nucleic acid delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are currently no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that would affect what is said herein.
Figures
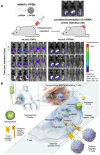
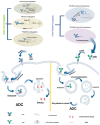

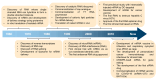
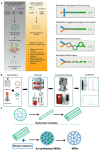

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 862401013154/Start-up fundings from Ocean University of China
- 862401013155/Start-up fundings from Ocean University of China
- LMDBCXRC202401/Laboratory for Marine Drugs and Bioproducts, Qingdao Marine Science and Technology Center
- LMDBCXRC202402/Laboratory for Marine Drugs and Bioproducts, Qingdao Marine Science and Technology Center
- tsqn202306102/Taishan Scholar Youth Expert Program of Shandong Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

