Disclosing the Novel Protective Mechanisms of Ocrelizumab in Multiple Sclerosis: The Role of PKC Beta and Its Down-Stream Targets
- PMID: 39201609
- PMCID: PMC11354964
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25168923
Disclosing the Novel Protective Mechanisms of Ocrelizumab in Multiple Sclerosis: The Role of PKC Beta and Its Down-Stream Targets
Abstract
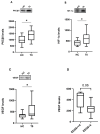
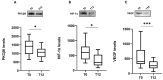
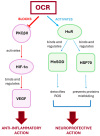
Ocrelizumab (OCR) is a humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody approved for both Relapsing and Primary Progressive forms of Multiple Sclerosis (MS) treatment. OCR is postulated to act via rapid B cell depletion; however, by analogy with other anti-CD20 agents, additional effects can be envisaged, such as on Protein Kinase C (PKC). Hence, this work aims to explore novel potential mechanisms of action of OCR in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from MS patients before and after 12 months of OCR treatment. We first assessed, up-stream, PKCβII and subsequently explored two down-stream pathways: hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1α)/vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and human antigen R (HuR)/manganese-dependent superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) and heat shock proteins 70 (HSP70). At baseline, higher levels of PKCβII, HIF-1α, and VEGF were found in MS patients compared to healthy controls (HC); interestingly, the overexpression of this inflammatory cascade was counteracted by OCR treatment. Conversely, at baseline, the content of HuR, MnSOD, and HSP70 was significantly lower in MS patients compared to HC, while OCR administration induced the up-regulation of these neuroprotective pathways. These results enable us to disclose the dual positive action of OCR: anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective. Therefore, in addition to B cell depletion, the effect of OCR on these molecular cascades can contribute to counteracting disease progression.
Keywords: HIF-1α; HSP70; HuR; MnSOD; VEGF; multiple sclerosis; ocrelizumab; protein kinase C.
Conflict of interest statement
Lara Ahmad reports travel expenses, speaker honoraria, and advisory board work from Novartis, Roche, and Merck. Giacomo Greeco reports travel expenses, speaker honoraria, and advisory board work from Novartis. Roberto Bergamaschi reports travel expenses, speaker honoraria, and advisory board work from Biogen, Merck Serono, Roche, Novartis, Celgene, Janssen, and Sanofi Genzyme. Elena Colombo reports travel expenses, speaker honoraria, and advisory board work from Sanofi, Biogen, Novartis, Merck, Roche, Bristol MS, Janssen, and Alexion.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evidence for novel cell defense mechanisms sustained by dimethyl fumarate in multiple sclerosis patients: the HuR/SOD2 cascade.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2022 Dec;68:104197. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2022.104197. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2022. PMID: 36270254
-
Real-world experience of ocrelizumab initiation in a diverse multiple sclerosis population.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2021 Aug;53:103021. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2021.103021. Epub 2021 May 19. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2021. PMID: 34077828
-
Immune Profiling Reveals the T-Cell Effect of Ocrelizumab in Early Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis.Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2023 Feb 21;10(3):e200091. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000200091. Print 2023 May. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2023. PMID: 36810163 Free PMC article.
-
A Milestone in Multiple Sclerosis Therapy: Monoclonal Antibodies Against CD20-Yet Progress Continues.Neurotherapeutics. 2021 Jul;18(3):1602-1622. doi: 10.1007/s13311-021-01048-z. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Neurotherapeutics. 2021. PMID: 33880738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ocrelizumab and Other CD20+ B-Cell-Depleting Therapies in Multiple Sclerosis.Neurotherapeutics. 2017 Oct;14(4):835-841. doi: 10.1007/s13311-017-0557-4. Neurotherapeutics. 2017. PMID: 28695471 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Manganese Superoxide Dismutase: Structure, Function, and Implications in Human Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jul 10;14(7):848. doi: 10.3390/antiox14070848. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40722952 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

