Nanoparticles-Delivered Circular RNA Strategy as a Novel Antitumor Approach
- PMID: 39201617
- PMCID: PMC11354327
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25168934
Nanoparticles-Delivered Circular RNA Strategy as a Novel Antitumor Approach
Abstract
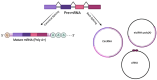
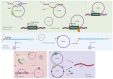
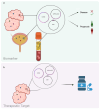
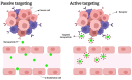
Anticancer therapy urgently needs the development of novel strategies. An innovative molecular target is represented by circular RNAs (circRNAs), single-strand RNA molecules with the 5' and 3' ends joined, characterized by a high stability. Although circRNA properties and biological functions have only been partially elucidated, their relationship and involvement in the onset and progression of cancer have emerged. Specific targeting of circRNAs may be obtained with antisense oligonucleotides and silencing RNAs. Nanotechnology is at the forefront of research for perfecting their delivery. Continuous efforts have been made to develop novel nanoparticles (NPs) and improve their performance, materials, and properties regarding biocompatibility and targeting capabilities. Applications in various fields, from imaging to gene therapy, have been explored. This review sums up the smart strategies developed to directly target circRNAs with the fruitful application of NPs in this context.
Keywords: cancer therapy; circRNA; circRNA-based therapeutic; drug delivery; gene therapy; nanomaterial; nanomedicine; nanoparticles; theranostics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zeng L., Yuan S., Zhou P., Gong J., Kong X., Wu M. Circular RNA Pvt1 oncogene (CircPVT1) promotes the progression of papillary thyroid carcinoma by activating the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway and modulating the ratio of microRNA-195 (miR-195) to vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) expression. Bioengineered. 2021;12:11795–11810. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2008639. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chaudhary R., Muys B.R., Grammatikakis I., De S., Abdelmohsen K., Li X.L., Zhu Y., Daulatabad S.V., Tsitsipatis D., Meltzer P.S., et al. A Circular RNA from the MDM2 Locus Controls Cell Cycle Progression by Suppressing p53 Levels. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2020;40:965–975. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00473-19. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou C., Li W., Liang Z., Wu X., Cheng S., Peng J., Zeng K., Li W., Lan P., Yang X., et al. Mutant KRAS-activated circATXN7 fosters tumor immunoescape by sensitizing tumor-specific T cells to activation-induced cell death. Nat. Commun. 2024;15:499. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-44779-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

