Antifungal Synergy: Mechanistic Insights into the R-1-R Peptide and Bidens pilosa Extract as Potent Therapeutics against Candida spp. through Proteomics
- PMID: 39201622
- PMCID: PMC11354716
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25168938
Antifungal Synergy: Mechanistic Insights into the R-1-R Peptide and Bidens pilosa Extract as Potent Therapeutics against Candida spp. through Proteomics
Abstract
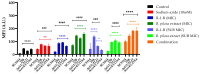
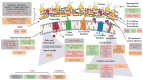
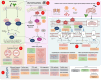
Previous reports have demonstrated that the peptide derived from LfcinB, R-1-R, exhibits anti-Candida activity, which is enhanced when combined with an extract from the Bidens pilosa plant. However, the mechanism of action remains unexplored. In this research, a proteomic study was carried out, followed by a bioinformatic analysis and biological assays in both the SC5314 strain and a fluconazole-resistant isolate of Candida albicans after incubation with R-1-R. The proteomic data revealed that treatment with R-1-R led to the up-regulation of most differentially expressed proteins compared to the controls in both strains. These proteins are primarily involved in membrane and cell wall biosynthesis, membrane transport, oxidative stress response, the mitochondrial respiratory chain, and DNA damage response. Additionally, proteomic analysis of the C. albicans parental strain SC5314 treated with R-1-R combined with an ethanolic extract of B. pilosa was performed. The differentially expressed proteins following this combined treatment were involved in similar functional processes as those treated with the R-1-R peptide alone but were mostly down-regulated (data are available through ProteomeXchange with identifier PXD053558). Biological assays validated the proteomic results, evidencing cell surface damage, reactive oxygen species generation, and decreased mitochondrial membrane potential. These findings provide insights into the complex antifungal mechanisms of the R-1-R peptide and its combination with the B. pilosa extract, potentially informing future studies on natural product derivatives.
Keywords: Bidens pilosa; Candida albicans; ROS; antifungal resistance; bovine lactoferricin peptides; disfunction mitochondrial; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures







References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

