The Regulation of MicroRNA-21 by Interleukin-6 and Its Role in the Development of Fibrosis in Endometriotic Lesions
- PMID: 39201680
- PMCID: PMC11354763
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25168994
The Regulation of MicroRNA-21 by Interleukin-6 and Its Role in the Development of Fibrosis in Endometriotic Lesions
Abstract
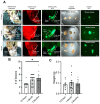
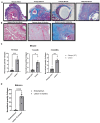
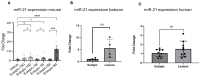
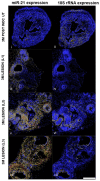
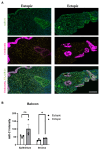
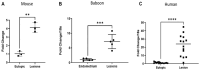
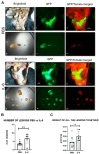
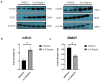
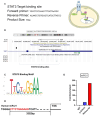
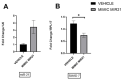
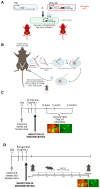
Endometriosis is one of the most common causes of chronic pelvic pain and infertility that affects 10% of women of reproductive age. It is currently defined as the presence of endometrial epithelial and stromal cells at ectopic sites; however, advances in endometriosis research have some authors believing that endometriosis should be re-defined as "a fibrotic condition in which endometrial stroma and epithelium can be identified". microRNAs (miRNAs) are regulatory molecules that potentially play a role in endometriotic lesion development. There is evidence that suggests that miRNAs, including microRNA-21 (miR-21), participate in fibrotic processes in different organs, including the heart, kidney, liver and lungs. The objective of this study was to understand the role of miR-21 and the mechanisms that can contribute to the development of fibrosis by determining how IL-6 regulates miR-21 expression and how this miRNA regulates the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) signaling pathway to promote fibrosis. We investigated the expression of miR-21 in the baboon and mouse model of endometriosis and its correlation with fibrosis. We demonstrated that inflammation and fibrosis are present at a very early stage of endometriosis and that the inflammatory environment in the peritoneal cavity, which includes interleukin 6 (IL-6), can regulate the expression of miR-21 in vitro and in vivo.
Keywords: IL-6; endometriosis; fibrosis; inflammation; microRNA-21.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

