Leveraging PARP-1/2 to Target Distant Metastasis
- PMID: 39201718
- PMCID: PMC11354653
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25169032
Leveraging PARP-1/2 to Target Distant Metastasis
Abstract
Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase (PARP) inhibitors have changed the outcomes and therapeutic strategy for several cancer types. As a targeted therapeutic mainly for patients with BRCA1/2 mutations, PARP inhibitors have commonly been exploited for their capacity to prevent DNA repair. In this review, we discuss the multifaceted roles of PARP-1 and PARP-2 beyond DNA repair, including the impact of PARP-1 on chemokine signalling, immune modulation, and transcriptional regulation of gene expression, particularly in the contexts of angiogenesis and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). We evaluate the pre-clinical role of PARP inhibitors, either as single-agent or combination therapies, to block the metastatic process. Efficacy of PARP inhibitors was demonstrated via DNA repair-dependent and independent mechanisms, including DNA damage, cell migration, invasion, initial colonization at the metastatic site, osteoclastogenesis, and micrometastasis formation. Finally, we summarize the recent clinical advancements of PARP inhibitors in the prevention and progression of distant metastases, with a particular focus on specific metastatic sites and PARP-1 selective inhibitors. Overall, PARP inhibitors have demonstrated great potential in inhibiting the metastatic process, pointing the way for greater use in early cancer settings.
Keywords: PARP inhibitors; PARP-1; PARP-2; cancer; metastasis; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
SH received speaker bureau fees from AstraZeneca-Merck, and advisory board honoraria from Exact Sciences.
Figures
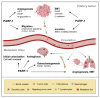
References
-
- Cancer Stat Facts: Female Breast Cancer. [(accessed on 14 July 2024)]; Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast.html.
-
- Cancer Stat Facts: Prostate Cancer. [(accessed on 14 July 2024)]; Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/prost.html.
-
- Cancer Stat Facts: Ovarian Cancer. [(accessed on 1 July 2024)]; Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/ovary.html.
-
- Cancer Stat Facts: Pancreatic Cancer. [(accessed on 14 July 2024)]; Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/pancreas.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

