Identification and Expression Analysis of Sulfate Transporter Genes Family and Function Analysis of GmSULTR3;1a from Soybean
- PMID: 39201766
- PMCID: PMC11354235
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25169080
Identification and Expression Analysis of Sulfate Transporter Genes Family and Function Analysis of GmSULTR3;1a from Soybean
Abstract
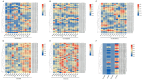
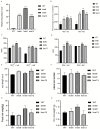
Sulfate transporters (SULTRs) are essential for the transport and absorption of sulfate in plants and serve as critical transport proteins within the sulfur metabolism pathway, significantly influencing plant growth, development, and stress adaptation. A bioinformatics analysis of SULTR genes in soybean was performed, resulting in the identification and classification of twenty-eight putative GmSULTRs into four distinct groups. In this study, the characteristics of the 28 GmSULTR genes, including those involved in collinearity, gene structure, protein motifs, cis-elements, tissue expression patterns, and the response to abiotic stress and plant hormone treatments, were systematically analyzed. This study focused on conducting a preliminary functional analysis of the GmSULTR3;1a gene, wherein a high expression level of GmSULTR3;1a in the roots, stems, and leaves was induced by a sulfur deficiency and GmSULTR3;1a improved the salt tolerance. A further functional characterization revealed that GmSULTR3;1a-overexpressing soybean hairy roots had higher SO42-, GSH, and methionine (Met) contents compared with the wild-type (WT) plant. These results demonstrate that the overexpression of GmSULTR3;1a may promote the sulfur assimilation metabolism and increase the content of sulfur-containing amino acids in plants.
Keywords: abiotic stress; soybean; sulfate transporter genes; sulfur nutrition; sulfur-containing amino acids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hernández L.E., Sobrino-Plata J., Montero-Palmero M.B., Carrasco-Gil S., Flores-Cáceres M.L., Ortega-Villasante C., Escobar C. Contribution of glutathione to the control of cellular redox homeostasis under toxic metal and metalloid stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2015;66:2901–2911. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv063. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

