Multi-Omics Integrative Analysis to Reveal the Impacts of Shewanella algae on the Development and Lifespan of Marine Nematode Litoditis marina
- PMID: 39201797
- PMCID: PMC11354469
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25169111
Multi-Omics Integrative Analysis to Reveal the Impacts of Shewanella algae on the Development and Lifespan of Marine Nematode Litoditis marina
Abstract
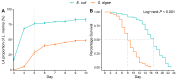
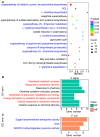
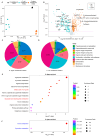
Understanding how habitat bacteria affect animal development, reproduction, and aging is essential for deciphering animal biology. Our recent study showed that Shewanella algae impaired Litoditis marina development and lifespan, compared with Escherichia coli OP50 feeding; however, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. Here, multi-omics approaches, including the transcriptome of both L. marina and bacteria, as well as the comparative bacterial metabolome, were utilized to investigate how bacterial food affects animal fitness and physiology. We found that genes related to iron ion binding and oxidoreductase activity pathways, such as agmo-1, cdo-1, haao-1, and tdo-2, were significantly upregulated in L. marina grown on S. algae, while extracellular structural components-related genes were significantly downregulated. Next, we observed that bacterial genes belonging to amino acid metabolism and ubiquinol-8 biosynthesis were repressed, while virulence genes were significantly elevated in S. algae. Furthermore, metabolomic analysis revealed that several toxic metabolites, such as puromycin, were enriched in S. algae, while many nucleotides were significantly enriched in OP50. Moreover, we found that the "two-component system" was enriched in S. algae, whereas "purine metabolism" and "one-carbon pool by folate" were significantly enriched in E. coli OP50. Collectively, our data provide new insights to decipher how diet modulates animal fitness and biology.
Keywords: Escherichia coli OP50; Litoditis marina; Shewanella algae; development; lifespan; metabolomics; transcriptomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Xue Y., Xie Y., Cao X., Zhang l. The marine natural microbiome mediates physiological outcomes in host nematodes. bioRxiv. 2023 doi: 10.1101/2023.05.10.540299. - DOI
-
- Poorbagher H., Lamare M.D., Barker M.F. Effects of nutrition on somatic growth and reproductive strategy of the sea urchin Pseudechinus huttoni. Mar. Biol. Res. 2010;6:292–301. doi: 10.1080/17451000903233797. - DOI
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- 32170537/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- COMS2019Q16/the Key deployment project of Centre for Ocean Mega-Research of Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences
- 16-8-3-19-zhc/the "Talents from overseas Program, IOCAS" of the Chinese Academy of Sciences; and the "Qingdao Innovation Leadership Program"
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

