Effect of Summer Holiday Programs on Children's Mental Health and Well-Being: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 39201822
- PMCID: PMC11352663
- DOI: 10.3390/children11080887
Effect of Summer Holiday Programs on Children's Mental Health and Well-Being: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
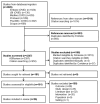
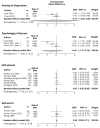
Poor youth mental health is an area of global concern. Summer holiday programs may provide environments that support mental health when the structures and supports of school are not available. The aim of this review was to determine the effectiveness of summer holiday programs in improving the mental health, social-emotional well-being, and cognitive (non-academic) outcomes of children and adolescents. Studies of summer holiday programs for school-aged children (5-18 years) were included if they measured any mental, socio-emotional or cognitive (non-academic) outcome. Studies were excluded if they were published prior to 2000, targeted clinical populations or lasted less than five days. Six databases were searched (April 2023). Risk of bias was assessed using the PEDro tool. Study outcomes were grouped according to three main constructs: mental health (psychological well-being, anxiety, depression, distress, and self-perception including self-esteem, self-worth, self-concept, confidence, and competence); social-emotional well-being (behavior and social skills, e.g., communication, bullying, conflict resolution, empathy, and social skills); and cognitive function (memory, selective attention, and executive function). A fourth "other" group captured substance use, personality traits, character skills, and values. Effect sizes were calculated as the standardized mean difference between pre- and post-intervention scores. The synthesis involved a random-effects meta-analysis (presented in forest plots), where possible, with the remaining outcomes narratively synthesized. Twenty-six studies (n = 6812 participants) were included. The results of the meta-analysis suggested that summer programs showed a statistically non-significant trend toward reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression (k = 2 studies, SMD = -0.17, 95% CI -2.94, 2.60), psychological distress (k = 2 studies, SMD -0.46, 95% CI -1.71, 0.79), and no effect on self-esteem (k = 6 studies, SMD = 0.02, 95% CI -0.02, 0.06) or self-worth (k = 3 studies, SMD = 0.05, 95% CI 0.00, 0.11). Narrative syntheses indicated a pattern toward improvements in general mental health, self-perception, social-emotional outcomes, and cognition. Studies were generally small, with a high risk of bias. Summer holiday programs for children and adolescents show trends toward improving mental, social, emotional, and cognitive outcomes. Programs targeting disadvantaged children showed stronger patterns of improvement related to mental health and self-perception than programs targeting the general population. While effect sizes are small to negligible, they consistently indicate improvements. Summer programs present a promising avenue to promote mental health in children; however, further rigorously designed, clearly reported control-group studies are required to more fully understand their effects.
Keywords: anxiety; children; cognition; depression; distress; mental health; summer camps; well-being.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organisation Mental Health. [(accessed on 16 July 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/mental-health-strengthe....
-
- Suldo S.M., Shaffer E.J. Looking Beyond Psychopathology: The Dual-Factor Model of Mental Health in Youth. Sch. Psychol. Rev. 2008;37:52–68. doi: 10.1080/02796015.2008.12087908. - DOI
-
- National Scientific Council on the Developing Child . Establishing a Level Foundation for Life: Mental Health Begins in Early Childhood. Harvard University, Center on the Developing Child; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2012.
-
- O’Connor M., Cloney D., Kvalsvig A., Goldfeld S. Positive Mental Health and Academic Achievement in Elementary School: New Evidence from a Matching Analysis. Educ. Res. 2019;48:205–216. doi: 10.3102/0013189X19848724. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous