Robotic-Assisted Surgery in Children Using the Senhance® Surgical System: An Observational Study
- PMID: 39201870
- PMCID: PMC11352959
- DOI: 10.3390/children11080935
Robotic-Assisted Surgery in Children Using the Senhance® Surgical System: An Observational Study
Abstract
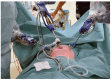
Background: Robotic-assisted surgery (RAS) holds many theoretical advantages, especially in pediatric surgical procedures. However, most robotic systems are dedicated to adult surgery and are less suitable for smaller children. The Senhance® Surgical System (SSS®), providing 3 mm and 5 mm instruments, focuses on making RAS technically feasible for smaller children. This prospective observational study aims to assess whether RAS in pediatric patients using the SSS® is safe and feasible.
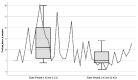
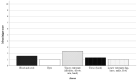
Methods and results: A total of 42 children (aged 0-17 years, weight ≥ 10 kg) underwent a RAS procedure on the abdominal area using the SSS® between 2020 and 2023. The study group consisted of 20 male and 22 female individuals. The mean age was 10.7 years (range 0.8 to 17.8 years), with a mean body weight of 40.7 kg (range 10.1 to 117.3 kg). The 3-mm-sized instruments of the SSS® were used in 12 of the 42 children who underwent RAS. The RAS procedures were successfully completed in 90% of cases. The conversion rate to conventional laparoscopy was low (10%), and there were no conversions to open surgery. One of the 42 cases (2%) experienced intraoperative complications, whereas six children (14%) suffered from a postoperative complication. Overall, 86% of the patients had an uncomplicated postoperative course.
Conclusions: The results of the current observational study demonstrate the safety and feasibility of utilizing the SSS® for abdominal pediatric RAS procedures. The study provides new fundamental information supporting the implementation of the SSS® in clinical practice in pediatric surgery.
Keywords: Senhance Surgical System; children; minimally invasive surgery; pediatric patients; robotic-assisted laparoscopy; robotic-assisted surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

