Neonatal Thyrotoxicosis in Infants of Mothers with Graves' Disease Treated for Radioiodine-Induced Hypothyroidism: A Literature Review
- PMID: 39201903
- PMCID: PMC11352502
- DOI: 10.3390/children11080968
Neonatal Thyrotoxicosis in Infants of Mothers with Graves' Disease Treated for Radioiodine-Induced Hypothyroidism: A Literature Review
Abstract
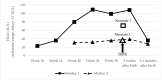
Fetal and neonatal thyrotoxicosis occurs in up to 5% of pregnancies in mothers with Graves' disease (GD). This condition is caused by stimulating antibodies against the thyrotropin receptor (TRAbs) that cross the placenta and may stimulate the fetal thyroid, typically in the second half of pregnancy. GD is often treated with radioiodine, resulting in hypothyroidism in most patients, but TRAbs can persist for several years. Even if a pregnant mother is hypothyroid after radioiodine therapy or surgery, her TRAbs can still, although rarely, induce fetal hyperthyroidism. In this review, we first present two cases of neonatal hyperthyroidism in mothers with GD who became hypothyroid after prior radioiodine therapy, identified through a 10-year analysis of the National Perinatal System in Slovenia. Based on these cases, we provide an overview of existing data on this rare clinical condition in neonates. We also discuss the underlying mechanisms and clinical outcomes based on currently available data. In conclusion, our review highlights the importance of careful monitoring during pregnancy in all women with GD, even in those well managed after radioiodine therapy or surgery.
Keywords: Graves’ disease; fetal thyrotoxicosis; neonatal thyrotoxicosis; radioiodine treatment; stimulating antibodies against thyrotropin receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources