Novel Surgical Technique for Total Knee Arthroplasty Integrating Kinematic Alignment and Real-Time Elongation of the Ligaments Using the NextAR System
- PMID: 39201986
- PMCID: PMC11355594
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm14080794
Novel Surgical Technique for Total Knee Arthroplasty Integrating Kinematic Alignment and Real-Time Elongation of the Ligaments Using the NextAR System
Abstract
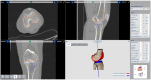
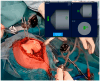
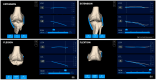
This study introduces an innovative surgical approach for total knee arthroplasty (TKA) that combines kinematic alignment (KA) principles with real-time elongation of the knee ligaments through the range of motion, using augmented reality (AR). The novelty of the surgical technique lies in the possibility of enhancing the decision-making process to perform the cut on the tibia as for the KA caliper technique developed by Dr. Stephen Howell. The NextAR is a CT-based AR system that offers the possibility of performing three-dimensional surgical preoperative planning and an accurate execution in the surgical room through single-use infrared sensors, smart glasses, and a control unit. During the preoperative planning, the soft tissue is not considered and only the alignment based on bony reference is ensured. Thanks to the possibility of measuring in real time the elongation of the knee collateral lateral ligaments, the system assists the surgeon in optimizing the cut on the tibia after an accurate resurfacing of the femur as described in the KA surgical technique. The implant used in this novel approach is a medial pivot design (Medacta GMK Sphere) that allows the restoration of the physiological behavior of the software tissue and natural knee kinematics. In conclusion, this novel technique offers a promising approach to TKA, allowing personalized treatment tailored to each patient's unique anatomy and soft tissue characteristics. The integration of KA and real-time soft tissue analysis provided by NextAR enhances surgical precision and outcomes, potentially improving patient satisfaction and functional results.
Keywords: NextAR; augmented reality; enabling technology; kinematic alignment; personalized arthroplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
L.S. is a paid consultant by Medacta International. Daniele Ascani works for Medacta International. Medacta had no role in the design, execution, or writing of this study. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Mancino F., Cacciola G., Malahias M.-A., De Filippis R., De Marco D., Di Matteo V., Gu A., Sculco P.K., Maccauro G., De Martino I. What are the benefits of robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty over conventional manual total knee arthroplasty? A systematic review of comparative studies. Orthop. Rev. 2020;12((Suppl. S1)):8657. doi: 10.4081/or.2020.8657. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hoveidaei A.H., Esmaeili S., Ghaseminejad-Raeini A., Pirahesh K., Fallahi M.S., Sandiford N.A., Citak M. Robotic assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is not associated with increased patient satisfaction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Orthop. 2024;48:1771–1784. doi: 10.1007/s00264-024-06206-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Auvinet E., Maillot C., Uzoho C. Augmented Reality Technology for Joint Replacement. In: Rivière C., Vendittoli P.A., editors. Personalized Hip and Knee Joint Replacement. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2020. pp. 321–328. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

