Long COVID Is Not a Functional Neurologic Disorder
- PMID: 39201991
- PMCID: PMC11355889
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm14080799
Long COVID Is Not a Functional Neurologic Disorder
Abstract
Long COVID is a common sequela of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Data from numerous scientific studies indicate that long COVID involves a complex interaction between pathophysiological processes. Long COVID may involve the development of new diagnosable health conditions and exacerbation of pre-existing health conditions. However, despite this rapidly accumulating body of evidence regarding the pathobiology of long COVID, psychogenic and functional interpretations of the illness presentation continue to be endorsed by some healthcare professionals, creating confusion and inappropriate diagnostic and therapeutic pathways for people living with long COVID. The purpose of this perspective is to present a clinical and scientific rationale for why long COVID should not be considered as a functional neurologic disorder. It will begin by discussing the parallel historical development of pathobiological and psychosomatic/sociogenic diagnostic constructs arising from a common root in neurasthenia, which has resulted in the collective understandings of myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) and functional neurologic disorder (FND), respectively. We will also review the case definition criteria for FND and the distinguishing clinical and neuroimaging findings in FND vs. long COVID. We conclude that considering long COVID as FND is inappropriate based on differentiating pathophysiologic mechanisms and distinguishing clinical findings.
Keywords: chronic fatigue syndrome; conversion disorder; dysautonomia; imaging; myalgic encephalomyelitis; neurasthenia; neurology; physical examination; post-COVID-19 condition (PCC); post-acute sequalae of COVID-19 (PASC).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
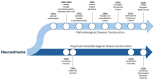
References
-
- Beard G. Neurasthenia, or nervous exhaustion. Boston Med. Surg. J. 1869;3:217–221. doi: 10.1056/NEJM186904290801301. - DOI
-
- Hickie I., Davenport T., Wakefield D., Vollmer-Conna U., Cameron B., Vernon S.D., Reeves W.C., Lloyd A., Dubbo Infection Outcomes Study Group Post-infective and chronic fatigue syndromes precipitated by viral and non-viral pathogens: Prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2006;333:575. doi: 10.1136/bmj.38933.585764.AE. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ikuta K., Yamada T., Shimomura T., Kuratsune H., Kawahara R., Ikawa S., Ohnishi E., Sokawa Y., Fukushi H., Hirai K., et al. Diagnostic evaluation of 2′, 5′-oligoadenylate synthetase activities and antibodies against Epstein-Barr virus and Coxiella burnetii in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome in Japan. Microbes Infect. 2003;5:1096–1102. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2003.07.002. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

