Effects of Dance-Based Aerobic Training on Mental Health and Quality of Life in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment
- PMID: 39202035
- PMCID: PMC11355123
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm14080844
Effects of Dance-Based Aerobic Training on Mental Health and Quality of Life in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment
Abstract
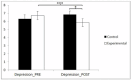
(1) Background: Mild cognitive impairment in older adults is a condition characterized by a decrease in mental abilities that affects their quality of life. The aim of this study is to evaluate the effects of an aerobic training program based on dance on depression, sleep quality, and quality of life in older adults with mild cognitive impairment. (2) Methods: This study employed a randomized controlled trial design with a total of 92 older adults with cognitive impairment, randomly assigned to an experimental group (n = 47) undergoing dance-based aerobic training and a control group (n = 45) who did not receive any intervention. Depression was assessed using the Yesavage Geriatric Depression Scale, sleep quality through the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), and quality of life through the SF-36 questionnaire. (3) Results: Statistically significant improvements were observed in depression (t(46) = 4.783, p = 0.000) and in the PSQI domains: subjective sleep quality (t(46) = 3.333, p = 0.002, and Cohen's d = 0.35), sleep duration (t(46) = 5.511, p = 0.000, and Cohen's d = 0.73) and PSQI total score (t(46) = 2.116, p = 0.040, and Cohen's d = 0.20). Regarding quality of life, improvements were observed in all domains of the questionnaire: the general health (t(46) = -9.374, p = 0.000, and Cohen's d = 0.03), physical function (t(46) = -9.374, p = 0.000, and Cohen's d = 0.03), the physical role (t(46) = -5.954, p = 0.000, and Cohen's d = 1.06), the emotional role (t(46) = -6.200, p = 0.000, and Cohen's d = 0.80), social function (t(46) = -5.585, p = 0.000, and Cohen's d = 0.53), physical pain, (t(46) = -9.224, p = 0.000, and Cohen's d = 1.04), vitality (t(46) = 2.289, p = 0.027, and Cohen's d = 1.27), mental health, (t(46) = -7.985, p = 0.000, and Cohen's d = 1.33), the physical summary component, (t(46) = -13.532, p = 0.000, and Cohen's d = 1.81), and in the mental summary component (t(46) = -10.6 81, p = 0.000, and Cohen's d = 0.06); (4) Conclusions: The results of the present study showed that they suggest that a dance-based aerobic training program improves mental health and quality of life in older people with mild cognitive impairment, providing a non-pharmacological approach to improve general well-being in this population.
Keywords: dance-based aerobics; depression; mild cognitive impairment; older adults; quality of life; sleep quality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Pais M., Martinez L., Ribeiro O., Loureiro J., Fernandez R., Valiengo L., Canineu P., Stella F., Talib L., Radanovic M., et al. Early diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: New definitions and challenges. Braz. J. Psychiatry. 2020;42:431–441. doi: 10.1590/1516-4446-2019-0735. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

