Assessment and Management of Maxillary Labial Frenum-A Scoping Review
- PMID: 39202198
- PMCID: PMC11352991
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14161710
Assessment and Management of Maxillary Labial Frenum-A Scoping Review
Abstract
Background: The maxillary labial frenum (MLF) is a soft tissue fold connecting the upper lip to the alveolar process. Abnormal attachment can cause periodontal, functional, and esthetic problems. Differential diagnosis is important and can prevent unnecessary interventions. This study aims to summarize the current evidence on the assessment and management of abnormal MLF.
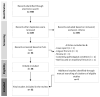
Methods: A thorough review of the literature was conducted. Five online databases were searched for relevant peer-reviewed human studies. Article screening and data extraction were performed independently by two reviewers using predefined inclusion/exclusion criteria. Information about article type, study design, participants' characteristics, interventions, and outcomes was extracted and synthesized.
Results: 52 articles met the review criteria. MLF is a dynamic structure characterized by a wide normal morphological variation. MLF assessment in infants has not been standardized. Studies in pre-adolescents reported a change in the thickness and position of the MLF observed over time, resulting in a lower prevalence of abnormal MLF morphology. Studies in adolescents and adults reported variable differential diagnosis criteria. Lasers appear as the most advantageous frenectomy modality.
Conclusions: There is a need for more objective MLF diagnostic protocols and treatment guidelines, which could prevent unnecessary surgical interventions.
Keywords: frenectomy; frenotomy; lip tie; maxillary frenum; upper lip frenum.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnosing and understanding the maxillary lip-tie (superior labial, the maxillary labial frenum) as it relates to breastfeeding.J Hum Lact. 2013 Nov;29(4):458-64. doi: 10.1177/0890334413491325. Epub 2013 Jul 2. J Hum Lact. 2013. PMID: 23821655
-
Maxillary Labial Frenum in Preschool Children: Variations, Anomalies and Associated Factors.J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2022 Jan 1;46(1):51-57. doi: 10.17796/1053-4625-46.1.9. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2022. PMID: 35311982
-
Longitudinal changes of the insertion of the maxillary labial frenum in children and adolescents undergoing orthodontic treatment.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2023 Jun;163(6):786-792. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2022.06.027. Epub 2023 Jan 16. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2023. PMID: 36653243
-
Upper Lip Tie and Breastfeeding: A Systematic Review.Breastfeed Med. 2019 Mar;14(2):83-87. doi: 10.1089/bfm.2018.0174. Epub 2019 Jan 25. Breastfeed Med. 2019. PMID: 30681376
-
The effect of frenectomy for tongue-tie, lip-tie, or cheek-tie on breastfeeding outcomes: A systematic review of articles over time and suggestions for management.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2023 Aug;171:111638. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2023.111638. Epub 2023 Jun 17. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 37352592
References
-
- Pandiyan N.J., Hedge A.M. Clinical assessment of frenum morphology and attachment in Malaysian children. Pesqui. Bras. Em Odontopediatria E Clin. Integr. 2018;18:3992. doi: 10.4034/PBOCI.2018.181.20. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous