Assessment of an Artificial Intelligence Tool for Estimating Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction in Echocardiograms from Apical and Parasternal Long-Axis Views
- PMID: 39202209
- PMCID: PMC11353168
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14161719
Assessment of an Artificial Intelligence Tool for Estimating Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction in Echocardiograms from Apical and Parasternal Long-Axis Views
Abstract
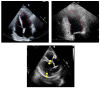
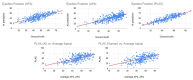
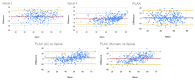
This work aims to evaluate the performance of a new artificial intelligence tool (ExoAI) to compute the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) in echocardiograms of the apical and parasternal long axis (PLAX) views. We retrospectively gathered echocardiograms from 441 individual patients (70% male, age: 67.3 ± 15.3, weight: 87.7 ± 25.4, BMI: 29.5 ± 7.4) and computed the ejection fraction in each echocardiogram using the ExoAI algorithm. We compared its performance against the ejection fraction from the clinical report. ExoAI achieved a root mean squared error of 7.58% in A2C, 7.45% in A4C, and 7.29% in PLAX, and correlations of 0.79, 0.75, and 0.89, respectively. As for the detection of low EF values (EF < 50%), ExoAI achieved an accuracy of 83% in A2C, 80% in A4C, and 91% in PLAX. Our results suggest that ExoAI effectively estimates the LVEF and it is an effective tool for estimating abnormal ejection fraction values (EF < 50%). Importantly, the PLAX view allows for the estimation of the ejection fraction when it is not feasible to acquire apical views (e.g., in ICU settings where it is not possible to move the patient to obtain an apical scan).
Keywords: artificial intelligence; echocardiogram; left ventricular ejection fraction; machine learning; ultrasound imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
Roberto Vega and Arun Nagdev are employees of Exo Imaging, whose AI software (Santa Clara, CA, USA, version 2.1.0) was used to perform the experiments. The other authors, who declare no conflicts of interests, had full access to the data, results, experiment details and analysis of the results.
Figures
References
-
- Olaisen S., Smistad E., Espeland T., Hu J., Pasdeloup D., Østvik A., Aakhus S., Rösner A., Malm S., Stylidis M., et al. Automatic measurements of left ventricular volumes and ejection fraction by artificial intelligence: Clinical validation in real time and large databases. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging. 2024;25:383–395. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jead280. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Loukas M., Burns D. Essential Ultrasound Anatomy. Wolters Kluwer; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2020. Basic Ultrasound Physics.
-
- Chen X., Yang F., Zhang P., Lin X., Wang W., Pu H., Chen X., Chen Y., Yu L., Deng Y., et al. Artificial Intelligence–Assisted Left Ventricular Diastolic Function Assessment and Grading: Multiview Versus Single View. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2023;36:1064–1078. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2023.07.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Asch F.M., Mor-Avi V., Rubenson D., Goldstein S., Saric M., Mikati I., Surette S., Chaudhry A., Poilvert N., Hong H., et al. Deep learning–based automated echocardiographic quantification of left ventricular ejection fraction: A point-of-care solution. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging. 2021;14:e012293. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.120.012293. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

