Anatomical Relationships of the Proximal Attachment of the Hamstring Muscles with Neighboring Structures: From Ultrasound, Anatomical and Histological Findings to Clinical Implications
- PMID: 39202213
- PMCID: PMC11353185
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14161725
Anatomical Relationships of the Proximal Attachment of the Hamstring Muscles with Neighboring Structures: From Ultrasound, Anatomical and Histological Findings to Clinical Implications
Abstract
Background: Injuries of the proximal attachment of the hamstring muscles are common. The present study aimed to investigate the relationship of the proximal attachment of the hamstring muscles with neighboring structures comprehensively.
Methods: A total of 97 hemipelvis from 66 cryopreserved specimens were evaluated via ultrasound, anatomical and histological samples.
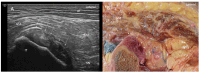
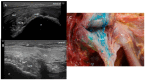
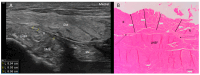
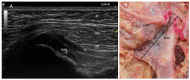
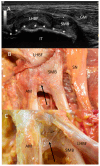
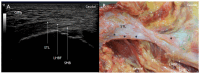
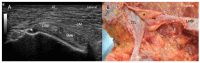
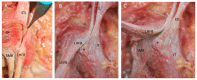
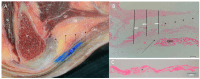
Results: The proximal attachment of the hamstring muscles presents a hyperechogenic line surrounding the origin of the semimembranosus and the long head of the biceps femoris muscles, as well as another hyperechogenic line covering the sciatic nerve. The anatomical and histological study confirms the ultrasound results and shows different layers forming the sacrotuberous ligament. Furthermore, it shows that the proximal attachment of the semimembranosus muscle has a more proximal origin than the rest of the hamstring muscles. Moreover, this muscle shares fibers with the long head of the biceps femoris muscle and expands to the adductor magnus muscle. The histological analysis also shows the dense connective tissue of the retinaculum covering the long head of the biceps femoris and semimembranosus muscles, as well as the expansion covering the sciatic nerve.
Conclusions: These anatomical relationships could explain injuries at the origin of the hamstring muscles.
Keywords: adductor magnus; biceps femoris; hamstring; ischial tuberosity; musculoskeletal; sacrotuberous ligament; sciatic nerve; tendinopathy; ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Anatomical study of the proximal origin of hamstring muscles.J Orthop Sci. 2012 Sep;17(5):614-8. doi: 10.1007/s00776-012-0243-7. Epub 2012 Jun 6. J Orthop Sci. 2012. PMID: 22669443
-
An anatomical and histological study of the structures surrounding the proximal attachment of the hamstring muscles.Man Ther. 2015 Jun;20(3):445-50. doi: 10.1016/j.math.2014.11.005. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Man Ther. 2015. PMID: 25515332
-
Hamstring Injury.2023 Aug 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2023 Aug 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 32644362 Free Books & Documents.
-
Sonographic landmarks in hamstring muscles.Skeletal Radiol. 2019 Nov;48(11):1675-1683. doi: 10.1007/s00256-019-03208-x. Epub 2019 Apr 17. Skeletal Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30997529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrasound Features of the Proximal Hamstring Muscle-Tendon-Bone Unit.J Ultrasound Med. 2019 May;38(5):1367-1382. doi: 10.1002/jum.14804. Epub 2018 Sep 27. J Ultrasound Med. 2019. PMID: 30260012 Review.
Cited by
-
Ultrasound Diagnosis of Hamstring Muscle Complex Injuries Focus on Originate Tendon Structure-Male University Rugby Players.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Dec 28;15(1):54. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15010054. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39795581 Free PMC article.
-
No difference in patient-reported outcomes between operative and non-operative management of proximal hamstring injuries, but return to sports is higher in operative treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Exp Orthop. 2025 Jul 13;12(3):e70327. doi: 10.1002/jeo2.70327. eCollection 2025 Jul. J Exp Orthop. 2025. PMID: 40655246 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Maniar N., Carmichael D.S., Hickey J.T., Timmins R.G., San Jose A.J., Dickson J., Opar D. Incidence and prevalence of hamstring injuries in field-based team sports: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 5952 injuries from over 7 million exposure hours. Br. J. Sports Med. 2023;57:109–116. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2021-104936. - DOI - PubMed

