Non-Operating Room Anesthesia (NORA) for Ultrasound-Guided Liver Radiofrequency Ablation
- PMID: 39202272
- PMCID: PMC11353362
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14161783
Non-Operating Room Anesthesia (NORA) for Ultrasound-Guided Liver Radiofrequency Ablation
Abstract
Introduction: Percutaneous ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a well-studied treatment option for locally non-advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and colorectal liver metastases (CRLMs). Sedation is of crucial interest as it enables safe and pain-free procedures. Whether the type of sedation has an impact on procedural outcome is still not well investigated.
Methods: We retrospectively collected data on patients undergoing liver RFA for various oncological conditions. Procedures were conducted in a non-operating room anesthesia (NORA) setting. Procedural-related complications and short-term oncological outcomes were analyzed.
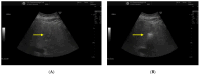
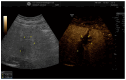
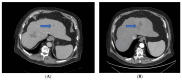
Results: Thirty-five patients (mean age 71.5 y, 80% male) were treated for HCC (26), CRLM (6) and gastric cancer metastases (3). Mean lesion size was 21 mm (SD ± 10.1 mm), and the most common tumor localization was the right hepatic lobe. RFA was performed in a step-up sedation approach, with subcutaneous lidocaine injection prior to needle placement and subsequent deep sedation during ablation. No anesthesia-related early or late complications occurred. One patient presented with pleural effusion due to a large ablation zone and was treated conservatively. Local tumor-free survival after 1 and 6 months was 100% in all cases where a curative RFA approach was intended.
Conclusions: NORA for liver RFA comes with high patient acceptance and tolerance, and optimal postoperative outcomes and oncologic results.
Keywords: deep sedation; hepatocellular carcinoma; non-operating room anesthesia (NORA); percutaneous liver radiofrequency ablation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors all declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cervantes A., Adam R., Roselló S., Arnold D., Normanno N., Taïeb J., Seligmann J., De Baere T., Osterlund P., Yoshino T., et al. Metastatic colorectal cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2023;34:10–32. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.10.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Reig M., Forner A., Rimola J., Ferrer-Fàbrega J., Burrel M., Garcia-Criado Á., Kelley R.K., Galle P.R., Mazzaferro V., Salem R., et al. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J. Hepatol. 2022;76:681–693. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.11.018. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

