Genetic and Phenotypic Spectrum of KMT2D Variants in Taiwanese Case Series of Kabuki Syndrome
- PMID: 39202303
- PMCID: PMC11353766
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14161815
Genetic and Phenotypic Spectrum of KMT2D Variants in Taiwanese Case Series of Kabuki Syndrome
Abstract
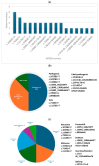
Kabuki syndrome (KS) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by distinct facial features, intellectual disability, and multiple congenital anomalies. We conducted a comprehensive analysis of the genetic and phenotypic spectrum of KS in a Taiwanese patient group of 23 patients. KMT2D variants were found in 22 individuals, with missense (26.1%), nonsense (21.7%), and frameshift (17.4%) variants being the most prevalent. One patient had a KMT2D variant of uncertain significance. The most common clinical characteristics included distinct facial features (100%), intellectual disability (100%), developmental delay (95.7%), speech delay (78.3%), hypotonia (69.6%), congenital heart abnormalities (69.6%), and recurrent infections (65.2%). Other abnormalities included hearing loss (39.1%), seizures (26.1%), cleft palate (26.1%), and renal anomalies (21.7%). This study broadens the mutational and phenotypic spectrum of KS in the Taiwanese population, highlighting the importance of comprehensive genetic testing and multidisciplinary clinical evaluations for diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: KMT2D; Kabuki syndrome; Taiwan; phenotypic heterogeneity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical and molecular analysis of Guangxi patients with Kabuki syndrome and KMT2D mutations.Heliyon. 2023 Sep 24;9(10):e20223. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20223. eCollection 2023 Oct. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37810849 Free PMC article.
-
Case Report: An Infant With Kabuki Syndrome, Alobar Holoprosencephaly and Truncus Arteriosus: A Case for Whole Exome Sequencing in Neonates With Congenital Anomalies.Front Genet. 2021 Nov 25;12:766316. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.766316. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34899850 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of genetic and phenotypic heterogeneity in 37 Turkish patients with Kabuki and Kabuki-like phenotype.Am J Med Genet A. 2022 Oct;188(10):2976-2987. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.62944. Epub 2022 Aug 8. Am J Med Genet A. 2022. PMID: 36097644
-
[One novel pathologic variation in KMT2D cause Kabuki syndrome with hearing loss as the main phenotype and related research on types of deafness].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Sep;33(9):820-824. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2019.09.006. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31446696 Review. Chinese.
-
Kabuki syndrome: clinical and molecular characteristics.Korean J Pediatr. 2015 Sep;58(9):317-24. doi: 10.3345/kjp.2015.58.9.317. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Korean J Pediatr. 2015. PMID: 26512256 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
- MMH-MM-113-13, MMH-E-113-13, MMH-MM-112-14, MMH-E-112-13, and MMH-E-111-13/Mackay Memorial Hospital
- NSTC-112-2314-B-195-014-MY3, NSTC-112-2811-B-195-001, NSTC-112-2314-B-195-003, NSTC-111-2314-B-195-017, NSTC-111-2811-B-195-002, NSTC-111-2811-B-195-001, NSTC-110-2314-B-195-014, NSTC-110-2314-B-195-010-MY3, and NSTC-110-2314-B-195-029/Ministry of Science and Technology
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

