Cognitive Impairment in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Is Associated with Corpus Callosum Microstructure Changes Based on Diffusion MRI
- PMID: 39202326
- PMCID: PMC11353603
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14161838
Cognitive Impairment in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Is Associated with Corpus Callosum Microstructure Changes Based on Diffusion MRI
Abstract
The cerebral small vessel disease (cSVD) is one of the main causes of vascular and mixed cognitive impairment (CI), and it is associated, in particular, with brain ageing. An understanding of structural tissue changes in an intact cerebral white matter in cSVD might allow one to develop the sensitive biomarkers for early diagnosis and monitoring of disease progression.
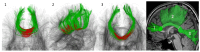
Purpose of the study: to evaluate microstructural changes in the corpus callosum (CC) using diffusion MRI (D-MRI) approaches in cSVD patients with different severity of CI and reveal the most sensitive correlations of diffusion metrics with CI.
Methods: the study included 166 cSVD patients (51.8% women; 60.4 ± 7.6 years) and 44 healthy volunteers (65.9% women; 59.6 ± 6.8 years). All subjects underwent D-MRI (3T) with signal (diffusion tensor and kurtosis) and biophysical (neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging, NODDI, white matter tract integrity, WMTI, multicompartment spherical mean technique, MC-SMT) modeling in three CC segments as well as a neuropsychological assessment.
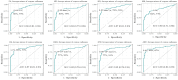
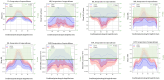
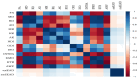
Results: in cSVD patients, microstructural changes were found in all CC segments already at the subjective CI stage, which was found to worsen into mild CI and dementia. More pronounced changes were observed in the forceps minor. Among the signal models FA, MD, MK, RD, and RK, as well as among the biophysical models, MC-SMT (EMD, ETR) and WMTI (AWF) metrics exhibited the largest area under the curve (>0.85), characterizing the loss of microstructural integrity, the severity of potential demyelination, and the proportion of intra-axonal water, respectively. Conclusion: the study reveals the relevance of advanced D-MRI approaches for the assessment of brain tissue changes in cSVD. The identified diffusion biomarkers could be used for the clarification and observation of CI progression.
Keywords: cognitive impairment; corpus callosum; diffusion models; small vessel disease; tract profiles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Disruption of corpus callosum microstructural integrity by diffusion MRI as a predictor of progression of cerebral microangiopathy].Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2023;123(11):95-104. doi: 10.17116/jnevro202312311195. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2023. PMID: 37994894 Russian.
-
Diffusion kurtosis imaging probes cortical alterations and white matter pathology following cuprizone induced demyelination and spontaneous remyelination.Neuroimage. 2016 Jan 15;125:363-377. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.10.052. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Neuroimage. 2016. PMID: 26525654 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of white matter tract integrity using diffusion kurtosis imaging reveals the correlation of white matter microstructural abnormalities with cognitive impairment in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Feb 29;15:1327339. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1327339. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38487342 Free PMC article.
-
White matter microstructure across the adult lifespan: A mixed longitudinal and cross-sectional study using advanced diffusion models and brain-age prediction.Neuroimage. 2021 Jan 1;224:117441. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117441. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Neuroimage. 2021. PMID: 33039618
-
The role of diffusion tensor imaging and fractional anisotropy in the evaluation of patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a literature review.Neurosurg Focus. 2016 Sep;41(3):E12. doi: 10.3171/2016.6.FOCUS16192. Neurosurg Focus. 2016. PMID: 27581308 Review.
References
-
- Cuadrado-Godia E., Dwivedi P., Sharma S., Ois Santiago A., Roquer Gonzalez J., Balcells M., Laird J., Turk M., Suri H.S., Nicolaides A., et al. Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: A Review Focusing on Pathophysiology, Biomarkers and Machine Learning Strategies. J. Stroke. 2018;20:302–320. doi: 10.5853/jos.2017.02922. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

