GhWRKY40 Interacts with an Asparaginase GhAPD6 Involved in Fiber Development in Upland Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.)
- PMID: 39202340
- PMCID: PMC11353873
- DOI: 10.3390/genes15080979
GhWRKY40 Interacts with an Asparaginase GhAPD6 Involved in Fiber Development in Upland Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.)
Abstract
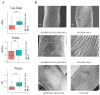
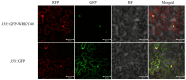
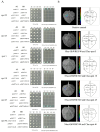
Fiber quality improvement is a primary goal in cotton breeding. Identification of fiber quality-related genes and understanding the underlying molecular mechanisms are essential prerequisites. Previously, studies determined that silencing the gene GhWRKY40 resulted in longer cotton fibers; however, both the underlying mechanisms and whether this transcription factor is additionally involved in the regulation of cotton fiber strength/fineness are unknown. In the current study, we verified that GhWRKY40 influences the fiber strength, fiber fineness, and fiber surface structure by using virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS). Potential proteins that may interact with the nucleus-localized GhWRKY40 were screened in a yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) nuclear-system cDNA library constructed from fibers at 0, 10, and 25 days post-anthesis (DPA) in two near-isogenic lines differing in fiber length and strength. An aspartyl protease/asparaginase-related protein, GhAPD6, was identified and confirmed by Y2H and split-luciferase complementation assays. The expression of GhAPD6 was approximately 30-fold higher in the GhWRKY40-VIGS lines at 10 DPA and aspartyl protease activity was significantly upregulated in the GhWRKY40-VIGS lines at 10-20 DPA. This study suggested that GhWRKY40 may interact with GhAPD6 to regulate fiber development in cotton. The results provide a theoretical reference for the selection and breeding of high-quality cotton fibers assisted by molecular technology.
Keywords: GhWRKY40; Gossypium hirsutum; aspartyl protease; fiber quality; split-luciferase complementation assay; yeast two-hybrid assay.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


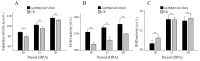
References
-
- Zou X., Liu A., Zhang Z., Ge Q., Fan S., Gong W., Li J., Gong J., Shi Y., Tian B., et al. Co-expression network analysis and hub gene selection for high-quality fiber in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) using RNA sequencing analysis. Genes. 2019;10:119. doi: 10.3390/genes10020119. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Si Z., Chen H., Zhu X., Cao Z., Zhang T. Genetic dissection of lint yield and fiber quality traits of G. hirsutum in G. barbadense background. Mol. Breed. 2017;37:9. doi: 10.1007/s11032-016-0607-3. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

