Role of Selected Genetic Polymorphisms in the Development of Rheumatoid Arthritis in a British White Population
- PMID: 39202369
- PMCID: PMC11354150
- DOI: 10.3390/genes15081009
Role of Selected Genetic Polymorphisms in the Development of Rheumatoid Arthritis in a British White Population
Abstract
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a complex autoimmune disease that negatively affects synovial joints, leading to the deterioration of movement and mobility of patients. This chronic disease is considered to have a strong genetic inheritance, with genome-wide association studies (GWAS) highlighting many genetic loci associated with the disease. Moreover, numerous confounding and non-genetic factors also contribute to the risk of the disease.
Aims: This study investigates the association of selected genetic polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis risk and develops a polygenic risk score (PRS) based on selected genes.
Methods: A case-control study recruited fully consenting participants from the East Midlands region of the UK. DNA samples were genotyped for a range of polymorphisms and genetic associations were calculated under several inheritance models. PRS was calculated at crude (unweighted) and weighted levels, and its associations with clinical parameters were determined.
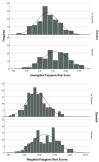
Results: There were significant associations with the risk of RA at six genetic markers and their associated risk alleles (TNRF2*G, TRAF1*A, PTPN22*T, HLA-DRB1*G, TNFα*A, and IL4-590*T). The TTG haplotype at the VDR locus increased the risk of RA with an OR of 3.05 (CI 1.33-6.98, p = 0.009). The GA haplotype of HLADRB1-TNFα-308 was a significant contributor to the risk of RA in this population (OR = 2.77, CI 1.23-6.28, p = 0.01), although linkage disequilibrium was low. The polygenic risk score was significantly higher in cases over controls in both unweighted (mean difference = 1.48, t285 = 5.387, p < 0.001) and weighted (mean difference = 2.75, t285 = 6.437, p < 0.001) results.
Conclusion: Several genetic loci contribute to the increased risk of RA in the British White sample. The PRS is significantly higher in those with RA and can be used for clinical applications and personalised prevention of disease.
Keywords: HLADRB1; IL4590; PTPN22; Polygenic Risk Score (PRS); TNFα; TRAF1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Investigation of Caucasian rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility loci in African patients with the same disease.Arthritis Res Ther. 2012 Nov 3;14(6):R239. doi: 10.1186/ar4082. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012. PMID: 23121884 Free PMC article.
-
Caucasian and Asian specific rheumatoid arthritis risk loci reveal limited replication and apparent allelic heterogeneity in north Indians.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31584. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031584. Epub 2012 Feb 15. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22355377 Free PMC article.
-
TRAF1 polymorphisms associated with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility in Asians and in Caucasians.Arthritis Rheum. 2009 Sep;60(9):2577-84. doi: 10.1002/art.24759. Arthritis Rheum. 2009. PMID: 19714643
-
Genetics of rheumatoid arthritis - a comprehensive review.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2013 Oct;45(2):170-9. doi: 10.1007/s12016-012-8346-7. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23288628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Progress of molecular genetics research on rheumatoid arthritis].Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2015 Oct;32(5):728-33. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1003-9406.2015.05.026. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26419001 Review. Chinese.
References
-
- NHS Symptoms-Rheumatoid Arthritis. [(accessed on 30 April 2024)]. Available online: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/rheumatoid-arthritis/symptoms/
-
- National Audit Office (NAO) Services for People with Rheumatoid Arthritis. National Audit Office (NAO); London, UK: 2009. [(accessed on 30 April 2024)]. Available online: https://www.nao.org.uk/reports/services-for-people-with-rheumatoid-arthr...
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Rheumatoid Arthritis. [(accessed on 30 April 2024)]. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng100/resources/rheumatoid-arthritis-in....
-
- Chang M., Rowland C.M., Garcia V.E., Schrodi S.J., Catanese J.J., van der Helm-van Mil A.H., Ardlie K.G., Amos C.I., Criswell L.A., Kastner D.L., et al. A Large-Scale Rheumatoid Arthritis Genetic Study Identifies Association at Chromosome 9q33.2. PLoS Genet. 2008;4:e1000107. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000107. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

