Changes in the Transcriptome and Long Non-Coding RNAs but Not the Methylome Occur in Human Cells Exposed to Borrelia burgdorferi
- PMID: 39202370
- PMCID: PMC11353914
- DOI: 10.3390/genes15081010
Changes in the Transcriptome and Long Non-Coding RNAs but Not the Methylome Occur in Human Cells Exposed to Borrelia burgdorferi
Abstract
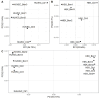
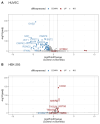
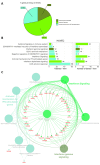
Lyme disease, caused by infection with members of the Lyme borreliosis group of Borrelia spirochete bacteria, is increasing in frequency and distribution worldwide. Epigenetic interactions between the mammalian host, tick, and bacterial pathogen are poorly understood. In this study, high-throughput next-generation sequencing (NGS) allowed for the in vitro study of the transcriptome, non-coding RNAs, and methylome in human host cells in response to Borrelia burgdorferi infection. We tested the effect of the Borrelia burgdorferi strain B31 on a human primary cell line (HUVEC) and an immortalized cell line (HEK-293) for 72 h, a long-duration time that might allow for epigenetic responses in the exposed human host cells. Differential gene expression was detected in both cell models in response to B. burgdorferi. More differentially expressed genes were found in HUVECs compared to HEK-293 cells. Borrelia burgdorferi exposure significantly induced genes in the interferon, in addition to cytokine and other immune response signaling in HUVECs. In HEK-293 cells, pre-NOTCH processing in Golgi was significantly downregulated in Borrelia-exposed cells. Other significantly altered gene expressions were found in genes involved in the extracellular matrix. No significant global methylation changes were detected in HUVECs or HEK-293 cells exposed to B. burgdorferi; however, two long non-coding RNAs and a pseudogene were deregulated in response to B. burgdorferi in HUVECs, suggesting that other epigenetic mechanisms may be initiated by infection.
Keywords: Borrelia burgdorferi; HEK-293 cells; HUVECs; Lyme disease; epigenetics; lncRNAs; transcriptome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
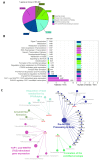
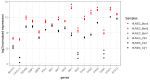
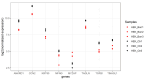
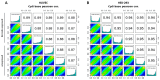

References
-
- De la Fuente J., Antunes S., Bonnet S., Cabezas-Cruz A., Domingos A.G., Estrada-Peña A., Johnson N., Kocan K.M., Mansfield K.L., Nijhof A.M., et al. Tick-Pathogen Interactions and Vector Competence: Identification of Molecular Drivers for Tick-Borne Diseases. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017;7:1–13. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00114. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Lyme Disease Charts and Figures: Historical Data. [(accessed on 18 May 2021)]; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/lyme/stats/graphs.html.
-
- Public Health Agency of Canada Surveillance of Lyme Disease. [(accessed on 18 May 2021)]. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/diseases/lyme-disease/su....
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

