Validation of Molecular Markers for Low Kunitz Trypsin Inhibitor Content in European Soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.) Germplasm
- PMID: 39202388
- PMCID: PMC11353867
- DOI: 10.3390/genes15081028
Validation of Molecular Markers for Low Kunitz Trypsin Inhibitor Content in European Soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.) Germplasm
Abstract
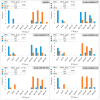
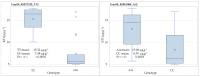
Trypsin inhibitors (TI) in raw soybean grain, mainly represented by the Kunitz trypsin inhibitor protein (KTI), prevent the normal activity of the digestive enzymes trypsin and chymotrypsin in humans and monogastric livestock. The inactivation of TI is achieved through costly and time-consuming heat treatment. Thermal processing also impairs the solubility and availability of the soybean grain protein. Therefore, the genetic elimination of KTI has been proposed as a suitable alternative to heat treatment. The aim of this study was to screen the collection of European soybean cultivars with six genetic markers (one SSR marker and five SNP markers) previously proposed as tightly linked to the KTI3 gene encoding the major Kunitz trypsin inhibitor seed protein of soybean and validate their usability for marker-assisted selection (MAS). The six markers were validated on a subset of 38 cultivars with wide variability in KTI content and in the F2 and F3:5 progenies of two crosses between the known high- and low-KTI cultivars. Three genetic markers (SSR Satt228 and two SNP markers, Gm08_45317135_T/G and Gm08_45541906_A/C) were significantly associated with KTI content in a subset of 38 cultivars. Low-KTI alleles were detected in both low- and high-KTI genotypes and vice versa, high-KTI alleles were found in both high- and low-KTI genotypes, indicating a tight but not perfect association of these markers with the KTI3 gene. The genetic marker SSR Satt228 showed a significant association with KTI content in the F2 progeny, while the SNP markers Gm08_45317135_T/G and Gm08_45541906_A/C allowed significant discrimination between progeny with high- vs. low-KTI progenies in the F3:5 generation. These three markers could be applied in MAS for low-KTI content but not without the additional phenotyping step to extract the desired low-KTI genotypes.
Keywords: Kuntz trypsin inhibitor; antinutrient; marker-assisted selection; soybean.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Development of Breeder-Friendly KASP Markers for Low Concentration of Kunitz Trypsin Inhibitor in Soybean Seeds.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 6;22(5):2675. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052675. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33800919 Free PMC article.
-
Introgression of null allele of Kunitz trypsin inhibitor through marker-assisted backcross breeding in soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.).BMC Genet. 2016 Jul 12;17(1):106. doi: 10.1186/s12863-016-0413-2. BMC Genet. 2016. PMID: 27407019 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic introgression and expression profiling of the KTI null allele in soybean through elite-by-elite backcrossing.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2025 Jul;224:109912. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2025.109912. Epub 2025 Apr 10. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40239262
-
Nutritional and health benefits of soy proteins.J Agric Food Chem. 2001 Mar;49(3):1069-86. doi: 10.1021/jf0009246. J Agric Food Chem. 2001. PMID: 11312815 Review.
-
Advancements in Inactivation of Soybean Trypsin Inhibitors.Foods. 2025 Mar 12;14(6):975. doi: 10.3390/foods14060975. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40232001 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- FAOSTAT Database. [(accessed on 7 June 2024)]. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL.
-
- Fraanje W., Garnett T. Soy: Food, Feed, and Land Use Change (Foodsource: Building Blocks). Food Climate Research Network. 2020. [(accessed on 7 June 2024)]. Available online: https://tabledebates.org/sites/default/files/2021-12/FCRN%20Building%20B....
-
- Liu K. Soybeans. Springer; Boston, MA, USA: 1997. Chemistry and nutritional value of soybean components; pp. 25–113.
-
- Nahashon S., Kilonzo-Nthenge A. Advances in soybean and soybean by-products in monogastric nutrition and health. In: El-Shemy H., editor. Soybean and Nutrition. IntechOpen; London, UK: 2011.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

