Genome-Wide Identification and Functional Analysis of the Genes of the ATL Family in Maize during High-Temperature Stress in Maize
- PMID: 39202465
- PMCID: PMC11353701
- DOI: 10.3390/genes15081106
Genome-Wide Identification and Functional Analysis of the Genes of the ATL Family in Maize during High-Temperature Stress in Maize
Abstract
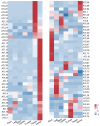
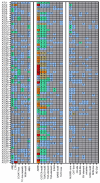
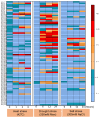
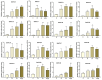
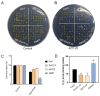
Maize is a significant food and feed product, and abiotic stress significantly impacts its growth and development. Arabidopsis Toxicosa en Levadura (ATL), a member of the RING-H2 E3 subfamily, modulates various physiological processes and stress responses in Arabidopsis. However, the role of ATL in maize remains unexplored. In this study, we systematically identified the genes encoding ATL in the maize genome. The results showed that the maize ATL family consists of 77 members, all predicted to be located in the cell membrane and cytoplasm, with a highly conserved RING domain. Tissue-specific expression analysis revealed that the expression levels of ATL family genes were significantly different in different tissues. Examination of the abiotic stress data revealed that the expression levels of ATL genes fluctuated significantly under different stress conditions. To further understand the biological functions of maize ATL family genes under high-temperature stress, we studied the high-temperature phenotypes of the maize ZmATL family gene ZmATL10 and its homologous gene AtATL27 in Arabidopsis. The results showed that overexpression of the ZmATL10 and AtATL27 genes enhanced resistance to high-temperature stress.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; Arabidopsis Toxicosa en Levadura; abiotic stress; gene family; heat stress; maize; tissue expression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Zhang Y., Gu J.-Y., Wang C., Wang W.-L., Zhang W.-Y., Gu J.-F., Liu L.-J., Yang J.-C., Zhang H. Carbon footprint of major grain crops in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River during 2011–2020. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2023;34:3364–3372. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202312.027. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

