Expression Pattern of PDE4B, PDE4D, and SFRP5 Markers in Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 39202484
- PMCID: PMC11356070
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina60081202
Expression Pattern of PDE4B, PDE4D, and SFRP5 Markers in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
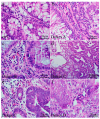
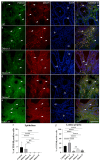
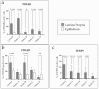
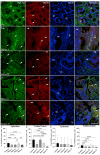
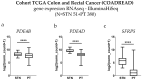
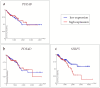
Background and Objectives: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the most frequently diagnosed malignant disease of the gastrointestinal system, and new diagnostic and prognostic markers are needed to elucidate the complete tumor profile. Materials and Methods: We used CRC tumor tissues (Dukes' A-D) and adjacent noncancerous tissues of 43 patients. Immunohistochemistry was used to examine the expression of phosphodiesterase 4B (PDE4B), phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D), and secreted frizzled related protein 5 (SFRP5) markers. We also analyzed the expression levels of PDE4B, PDE4D, and SFRP5 in CRC tissues compared to control tissues using RNA-sequencing data from the UCSC Xena browser. Results: In CRC stages, the distribution of PDE4B-positive cells varied, with differing percentages between epithelium and lamina propria. Statistically significant differences were found in the number of PDE4B-positive epithelial cells between healthy controls and all CRC stages, as well as between different CRC stages. Similarly, significant differences were observed in the number of PDE4B-positive cells in the lamina propria between healthy controls and all CRC stages, as well as between different CRC stages. CRC stage Dukes' C exhibited a significantly higher number of PDE4B-positive cells in the lamina propria compared to CRC stage Dukes' B. Significant differences were noted in the number of PDE4D-positive epithelial cells between healthy controls and CRC stages Dukes' A, B, and D, as well as between CRC stage Dukes' C and stages A, B, and D. CRC stage Dukes' A had significantly more PDE4D-positive cells in the lamina propria compared to stage D. Significant differences were also observed in the number of SFRP5-positive cells in the lamina propria between healthy controls and all CRC stages, as well as between CRC stages Dukes' A and D. While the expression of PDE4D varied across CRC stages, the expression of SFRP5 remained consistently strong in both epithelium and lamina propria, with significant differences noted mainly in the lamina propria. The expression levels of PDE4B, PDE4D, and SFRP5 reveal significant differences in the expression of these genes between CRC patients and healthy controls, with notable implications for patient prognosis. Namely, our results demonstrate that PDE4B, PDE4D, and SFRP5 are significantly under-expressed in CRC tissues compared to control tissues. The Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and the log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test revealed distinct prognostic implications where patients with lower expression levels of SFRP5 exhibited significantly longer overall survival. The data align with our immunohistochemical results and might suggest a potential tumor-suppressive role for these genes in CRC. Conclusions: Considering significantly lower gene expression, aligned with our immunohistochemical data in tumor tissue in comparison to the control tissue, as well as the significantly poorer survival rate in the case of its higher expression, we can hypothesize that SFRP5 is the most promising biomarker for CRC out of the observed proteins. These findings suggest alterations in PDE4B, PDE4D, and SFRP5 expression during CRC progression, as well as between different stages of CRC, with potential implications for understanding the molecular mechanisms involved in CRC development and progression.
Keywords: PDE4B; PDE4D; SFRP5; colorectal cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

