A Systematic Review Evaluating the Diagnostic Efficacy of Narrow-Band Imaging for Laryngeal Cancer Detection
- PMID: 39202487
- PMCID: PMC11356235
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina60081205
A Systematic Review Evaluating the Diagnostic Efficacy of Narrow-Band Imaging for Laryngeal Cancer Detection
Abstract
Background: Narrow-band imaging is an advanced endoscopic technology used to detect changes on the laryngeal tissue surface, employing a comparative approach alongside white-light endoscopy to facilitate histopathological examination. Objective: This study aimed to assess the utility and advantages of NBI (narrow-band imaging) in identifying malignant laryngeal lesions through a comparative analysis with histopathological examination. Methods: We conducted a systematic literature review, utilizing databases such as PubMed, the CNKI database, and Embase for our research. Results: We analyzed the articles by reviewing their titles and abstracts, selecting those we considered relevant based on determined criteria; in the final phase, we examined the relevant studies according to the specific eligibility criteria. Conclusions: Narrow-band imaging is an advanced endoscopic technology that demonstrates its efficacy as a tool for diagnosing malignant laryngeal lesions and comparing them to premalignant lesions. The European Society of Laryngology has implemented a standardized classification system for laryngeal lesions to enhance data correlation and organization.
Keywords: NBI; laryngeal cancer; laryngeal carcinoma; laryngeal neoplasms; larynx cancer; larynx carcinoma; narrow-band imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
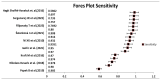
References
-
- Zhang J., Wu J., Yang Y., Liao H., Xu Z., Hamblin L.T., Jiang L., Depypere L., Ang K.L., He J., et al. White light, autofluorescence and narrow-band imaging bronchoscopy for diagnosing airway pre-cancerous and early cancer lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016;8:3205–3216. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2016.11.61. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

