Reinitiating Chemotherapy beyond Progression after Maintenance Immunotherapy in Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 39202506
- PMCID: PMC11356350
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina60081225
Reinitiating Chemotherapy beyond Progression after Maintenance Immunotherapy in Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
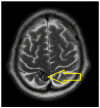
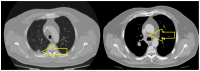
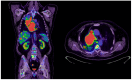
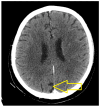
Introduction: Small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive form of cancer with a poor prognosis. The two-year survival rate is 8% of all cases. Case presentation: We present the case of a male patient who was 50 years old at the time of diagnosis in May 2022. He was diagnosed with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer, treated with immunotherapy in combination with chemotherapy (Durvalumab in combination with Etoposide plus Carboplatin) as a first-line treatment, followed by maintenance immunotherapy. In December 2023, a PET-CT scan revealed progressive disease with multiple metastases. Chemotherapy was reinitiated with Etoposide plus Cisplatin in January 2024. After two cycles of chemotherapy, the patient developed post-chemotherapy anemia, for which treatment with Epoetinum alpha was initiated. Chemotherapy was continued for another five cycles, until May 2024, with the maintenance of hemoglobin at a level within 9.9 mg/dL-11 mg/dL. Upon assessment at the end of May 2024, the patient presented an ECOG = 2 performance status, with a moderate general state, moderate-intensity fatigue, no pain, no anxiety or depression and no dyspnea. Discussions, Literature Review and Conclusions: Reinitiating chemotherapy after the failure of maintenance immunotherapy may be an option in patients with SCLC. Epoetinum allows oncological treatment by preventing chemotherapy-induced anemia.
Keywords: Epoetinum alpha; first-line immunotherapy; reinitiating chemotherapy; small-cell lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


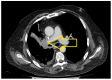
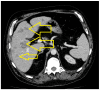
Similar articles
-
Durvalumab, with or without tremelimumab, plus platinum-etoposide versus platinum-etoposide alone in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): updated results from a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2021 Jan;22(1):51-65. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30539-8. Epub 2020 Dec 4. Lancet Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33285097 Clinical Trial.
-
Durvalumab plus platinum-etoposide versus platinum-etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial.Lancet. 2019 Nov 23;394(10212):1929-1939. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32222-6. Epub 2019 Oct 4. Lancet. 2019. PMID: 31590988 Clinical Trial.
-
Durvalumab: A Review in Extensive-Stage SCLC.Target Oncol. 2021 Nov;16(6):857-864. doi: 10.1007/s11523-021-00843-0. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Target Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34731446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cisplatin, Etoposide, and Bevacizumab Regimen Followed by Oral Etoposide and Bevacizumab Maintenance Treatment in Patients With Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Single-Institution Experience.Clin Lung Cancer. 2015 Nov;16(6):e229-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2015.05.005. Epub 2015 May 18. Clin Lung Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26072097
-
Use of Immunotherapy in Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer.Oncology. 2020;98(11):749-754. doi: 10.1159/000508516. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Oncology. 2020. PMID: 32663833 Review.
References
-
- Dawe D.E., Rittberg R., Syed I., Shanahan M.K., Moldaver D., Bucher O., Galloway K., Reynolds K., Paul J.T., Harlos C., et al. Real-world predictors of survival in patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer in Manitoba, Canada: A retrospective cohort study. Front. Oncol. 2023;13:1191855. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1191855. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Basumallik N., Agarwal M. StatPearls [Internet] StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2024. Small Cell Lung Cancer. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

