Novel Immunohistochemical and Morphological Approaches in a Retrospective Study of Post-Mortem Myocarditis
- PMID: 39202593
- PMCID: PMC11356551
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina60081312
Novel Immunohistochemical and Morphological Approaches in a Retrospective Study of Post-Mortem Myocarditis
Abstract
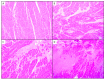
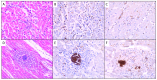
Background and Objectives: This study presents a retrospective analysis of 26 autopsy cases from a single centre, primarily focusing on forensic cases, with a majority of male individuals. Materials and Methods: We systematically analysed autopsy reports and cardiac tissue slides using haematoxylin-eosin stain and immunohistochemistry for CD3, CD163, and IL-6. The histological assessment evaluated key variables such as inflammation severity, necrosis, and background changes using a standardised grading system. Quantitative analysis of immunohistochemical markers was performed, calculating the percentage of positively stained cells within the inflammatory infiltrate. Results: The average age was 51.6 years, slightly skewed towards older males. The fatalities varied widely, with sudden death and drug abuse being the most common conditions linked to myocarditis findings on histological examination. A strong correlation was found between the severity of inflammation (measured by size within a myocardium section) and the scoring system based on the number of inflammatory foci per section (p ≤ 0.001). Most cases showed mild to minimal fibrosis, with some exhibiting moderate to severe fibrosis, arteriosclerosis, and myocyte hypertrophy. The presence of protein CD3 in the inflammatory infiltrate revealed a moderate inverse correlation between the CD3 values and the severity of inflammation and necrosis, and a strong inverse correlation with neutrophil levels. CD3 levels were higher in sudden death cases and lower in cases with numerous inflammatory foci, highlighting the discreet nature of lymphocytic myocarditis. Macrophage presence, assessed using CD163, showed a moderate inverse correlation with neutrophil levels and significant differences between sudden death and non-sudden death cases. Macrophage-rich inflammation was observed in cases with pneumonia/bronchopneumonia-associated lesions. IL-6 expression showed a moderate direct correlation with inflammation severity (p = 0.028), severity of necrosis (p = 0.005), and the number of inflammatory foci per section (p = 0.047). A moderate inverse correlation was found between CD3 and IL-6 expression (p = 0.005). Conclusions: These findings highlight the need for a unique immunohistochemical approach in forensic cases of myocarditis, differing from guidelines for endomyocardial biopsies due to diverse inflammatory cells. The study suggests exploring inflammatory chemokines within myocarditis foci for their significance in clinical scenarios. Specifically, IL-6, a crucial pro-inflammatory interleukin, correlated significantly with the severity of inflammation and necrosis (p < 0.05). This study provides novel and valuable insights into the histopathological and immunological markers of myocarditis in autopsy cases.
Keywords: CD163; CD3; forensic pathology; immunohistochemistry; interleukin 6; myocarditis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
CD45 is a more sensitive marker than CD3 to diagnose lymphocytic myocarditis in the endomyocardium.Hum Pathol. 2017 Apr;62:83-90. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2016.11.006. Epub 2016 Dec 23. Hum Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28025077
-
Immunohistochemical diagnosis of myocarditis on (infantile) autopsy material: Does it improve the diagnosis?Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2015 Jun;11(2):168-76. doi: 10.1007/s12024-015-9675-7. Epub 2015 Apr 17. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25894115
-
COVID-19 myocarditis: quantitative analysis of the inflammatory infiltrate and a proposed mechanism.Cardiovasc Pathol. 2021 Sep-Oct;54:107361. doi: 10.1016/j.carpath.2021.107361. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2021. PMID: 34174415 Free PMC article.
-
Sudden death related myocarditis: a study of 56 cases.Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2010 Mar;6(1):13-9. doi: 10.1007/s12024-009-9125-5. Epub 2009 Nov 29. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20091145
-
[Dilated cardiomyopathy--a chronic myocarditis? New aspects on diagnosis and therapy].Z Kardiol. 1993;82 Suppl 4:25-32. Z Kardiol. 1993. PMID: 8147059 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Speckle Tracking Analysis of Right Ventricle Function in Myocarditis with Preserved Right Ventricular Ejection Fraction.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Sep 25;60(10):1569. doi: 10.3390/medicina60101569. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39459355 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Caforio A.L., Calabrese F., Angelini A., Tona F., Vinci A., Bottaro S., Ramondo A., Carturan E., Iliceto S., Thiene G., et al. A prospective study of biopsy-proven myocarditis: Prognostic relevance of clinical and aetiopathogenetic features at diagnosis. Eur. Heart J. 2007;28:1326–1333. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehm076. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Caforio A.L.P., Pankuweit S., Arbustini E., Basso C., Gimeno-Blanes J., Felix S.B., Fu M., Heliö T., Heymans S., Jahns R., et al. Current state of knowledge on aetiology, diagnosis, management, and therapy of myocarditis: A position statement of the European Society of Cardiology Working Group on Myocardial and Pericardial Diseases. Eur. Heart J. 2013;34:2636–2648. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht210. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

