Introducing and Boosting Oxygen Vacancies within CoMn2O4 by Loading on Planar Clay Minerals for Efficient Peroxymonosulfate Activation
- PMID: 39202904
- PMCID: PMC11357143
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29163825
Introducing and Boosting Oxygen Vacancies within CoMn2O4 by Loading on Planar Clay Minerals for Efficient Peroxymonosulfate Activation
Abstract
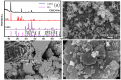
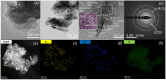
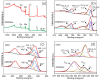
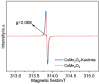
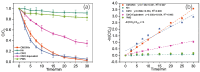
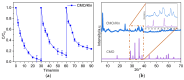
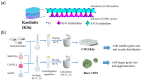
CoMn2O4 (CMO) has been recognized as an effective peroxymonosulfate (PMS) activator; however, it still shows disadvantages such as limited reactive sites and metal leakage. Herein, an effective and environmentally friendly composite catalyst, CMO/Kln, was synthesized by anchoring CMO on kaolinite (Kln), a natural clay mineral with a special lamellar structure, to activate peroxymonosulfate (PMS) for the degradation of residue pharmaceuticals in water. The abundant hydroxyl groups located on the surface of Kln helped induce rich oxygen vacancies (OVs) into composite CMO/Kln, which not only acted as additional active sites but also accelerated working efficiency. In addition, compared with bare CMO, CMO/Kln showed lower crystallinity, and the adoption of the Kln substrate contributed to its structural stability with lower metal leaching after three rounds of reaction. The universal applicability of CMO/Kln was also verified by using three other pharmaceuticals as probes. This work shed light on the adoption of natural clay minerals in modifying CMO catalysts with promoted catalytic activity for the efficient and eco-friendly remediation of pharmaceuticals in wastewater.
Keywords: CoMn2O4; composite catalyst; kaolinite; peroxymonosulfate activation; pharmaceutical degradation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Controlling oxygen vacancies of CoMn2O4 by loading on planar and tubular clay minerals and its application for boosted PMS activation.J Hazard Mater. 2022 Aug 15;436:129060. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129060. Epub 2022 May 5. J Hazard Mater. 2022. PMID: 35594679
-
Non-radical-dominated catalytic degradation of methylene blue by magnetic CoMoO4/CoFe2O4 composite peroxymonosulfate activators.J Environ Manage. 2023 Jan 1;325(Pt B):116587. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116587. Epub 2022 Oct 28. J Environ Manage. 2023. PMID: 36323118
-
Activation of peroxymonosulfate by a floating oxygen vacancies - CuFe2O4 photocatalyst under visible light for efficient degradation of sulfamethazine.Sci Total Environ. 2022 Jun 10;824:153630. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153630. Epub 2022 Feb 14. Sci Total Environ. 2022. PMID: 35176364
-
Ultrafast short-range catalytic pathway modified peroxymonosulfate activation over CuO with surface oxygen defects for tetracycline hydrochloride degradation.Environ Res. 2023 Apr 1;222:115322. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.115322. Epub 2023 Jan 21. Environ Res. 2023. PMID: 36693467
-
Peroxymonosulfate activation by oxygen vacancies-enriched MXene nano-Co3O4 co-catalyst for efficient degradation of refractory organic matter: Efficiency, mechanism, and stability.J Hazard Mater. 2022 Jun 15;432:128719. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128719. Epub 2022 Mar 17. J Hazard Mater. 2022. PMID: 35325862
References
-
- Stackelberg P.E., Furlong E.T., Meyer M.T., Zaugg S.D., Henderson A.K., Reissman D.B. Persistence of pharmaceutical compounds and other organic wastewater contaminants in a conventional drinking-water-treatment plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2004;329:99–113. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.03.015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen H., Xu Y., Zhu K., Zhang H. Understanding oxygen-deficient La2CuO4-δ perovskite activated peroxymonosulfate for bisphenol A degradation: The role of localized electron within oxygen vacancy. Appl. Catal. B. 2021;284:119732. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119732. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

