Phytochemical Analysis, Biological Activities, and Docking of Phenolics from Shoot Cultures of Hypericum perforatum L. Transformed by Agrobacterium rhizogenes
- PMID: 39202972
- PMCID: PMC11357161
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29163893
Phytochemical Analysis, Biological Activities, and Docking of Phenolics from Shoot Cultures of Hypericum perforatum L. Transformed by Agrobacterium rhizogenes
Abstract
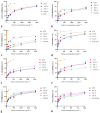
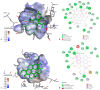
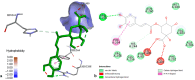
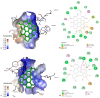
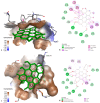
Hypericum perforatum transformed shoot lines (TSL) regenerated from corresponding hairy roots and non-transformed shoots (NTS) were comparatively evaluated for their phenolic compound contents and in vitro inhibitory capacity against target enzymes (monoamine oxidase-A, cholinesterases, tyrosinase, α-amylase, α-glucosidase, lipase, and cholesterol esterase). Molecular docking was conducted to assess the contribution of dominant phenolic compounds to the enzyme-inhibitory properties of TSL samples. The TSL extracts represent a rich source of chlorogenic acid, epicatechin and procyanidins, quercetin aglycone and glycosides, anthocyanins, naphthodianthrones, acyl-phloroglucinols, and xanthones. Concerning in vitro bioactivity assays, TSL displayed significantly higher acetylcholinesterase, tyrosinase, α-amylase, pancreatic lipase, and cholesterol esterase inhibitory properties compared to NTS, implying their neuroprotective, antidiabetic, and antiobesity potential. The docking data revealed that pseudohypericin, hyperforin, cadensin G, epicatechin, and chlorogenic acid are superior inhibitors of selected enzymes, exhibiting the lowest binding energy of ligand-receptor complexes. Present data indicate that H. perforatum transformed shoots might be recognized as an excellent biotechnological system for producing phenolic compounds with multiple health benefits.
Keywords: Hypericum perforatum; biological activities; molecular docking; phenolic compounds; transformed shoots.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Rafailovska E., Tushevski O., Shijakova K., Simic S.G., Kjovkarovska S.D., Miova B. Hypericum perforatum L. extract exerts insulinotropic effects and inhibits gluconeogenesis in diabetic rats by regulating AMPK expression and PKCε concentration. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023;302:115899. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115899. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kapoor S., Chandel R., Kaur R., Kumar S., Kumar R., Janghu S., Kaur A., Kumar V. The Flower of Hypericum perforatum L.: A traditional source of bioactives for new food and pharmaceutical applications. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2023;110:104702. doi: 10.1016/j.bse.2023.104702. - DOI
-
- Shasmita Behera S., Mishra P., Samal M., Mohapatra D., Monalisa K., Naik S.K. Recent advances in tissue culture and secondary metabolite production in Hypericum perforatum L. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2023;154:13–28. doi: 10.1007/s11240-023-02525-3. - DOI
-
- Ion V., Ielciu I., Cârje A.G., Muntean D.L., Crişan G., Păltinean R. Hypericum spp.—An Overview of the Extraction Methods and Analysis of Compounds. Separations. 2022;9:17. doi: 10.3390/separations9010017. - DOI
-
- Silva A.R., Taofiq O., Ferreira I.C., Barros L. Hypericum genus cosmeceutical application–A decade comprehensive review on its multifunctional biological properties. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021;159:113053. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.113053. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

