Ti/CuO Nanothermite-Study of the Combustion Process
- PMID: 39203011
- PMCID: PMC11357317
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29163932
Ti/CuO Nanothermite-Study of the Combustion Process
Abstract
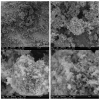
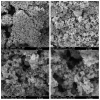
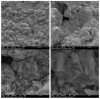
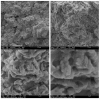
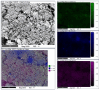
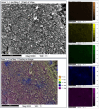
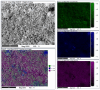
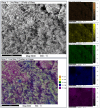
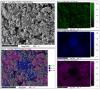
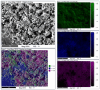
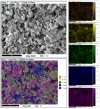
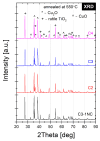
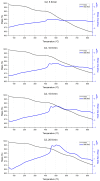
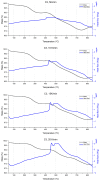
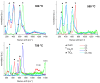
A study of the combustion processes of Ti/CuO and Ti/CuO/NC nanothermites prepared via electrospraying was conducted in this work. For this purpose, the compositions were thermally conditioned at 350, 550 and 750 °C, as selected based on our initial differential scanning calorimetry-thermogravimetry (DSC/TG) investigations. The tested compositions were analysed for chemical composition and morphology using SEM-EDS, Raman spectroscopy and XRD measurements. Additionally, the thermal behaviour and decomposition kinetics of compositions were explored by means of DSC/TG. The Kissinger and Ozawa methods were applied to the DSC curves to calculate the reaction activation energy. SEM-EDS analyses indicated that sintering accelerated with increasing equivalence ratio and there was a strong effect on the sintering process due to cellulose nitrate (NC) addition. The main combustion reaction was found to start at 420-450 °C, as confirmed by XRD and Raman study of samples annealed at 350 °C and 550 °C. Moreover, increasing the fuel content in the composition led to lower Ea, higher reaction heats and a more violent combustion process. Conversely, the addition of NC had an ambiguous effect on Ea. Finally, a multi-step combustion mechanism was proposed and is to some extent in line with the more general reactive sintering (RS) mechanism. However, unusual mass transfer was observed, i.e., to the fuel core, rather than the opposite, which is typically observed for Al-based nanothermites.
Keywords: combustion; energetic material; nanothermite.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures































References
-
- Dixon G.P., Martin J.A., Thompson D. Lead-Free Precussion Primer Mixes Based on Metastable Interstitial Composite (MIC) Technology. 5,717,159. U.S. Patent. 1998 February 10;
-
- Nicollet A., Charlot S., Baijot V., Estève A., Rossi C. Ultra-rapid and fully integrated active pyrotechnic safety switches integrating nanothermites; Proceedings of the 2017 Materials Research Society Fall Meeting & Exhibit; Boston, MA, USA. 26 November–1 December 2017.
-
- Ru C., Wang F., Xu J., Dai J., Shen Y., Ye Y., Zhu P., Shen R. Superior performance of a MEMS-based solid propellant microthruster (SPM) array with nanothermites. Microsyst. Technol. 2017;23:3161–3174.
-
- Comet M., Martin C., Schnell F., Spitzer D. Nanothermites: A short review. Factsheet for experimenters, present and future challenges. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2019;44:18–36.
-
- Lopez A., Drukier A., Freese K., Kurdak C., Tarle G. New dark matter detector using nanoscale explosives. arXiv. 20141403.8115
Grants and funding
- DWD/4/21/2020-51/003/Ministry of Science and Higher Education
- POIR.04.02.00-00-B003/18/National Centre for Research and Development
- M-ERA.NET3/2021/93/HYDROSENS/2022/National Centre for Research and Development
- project 9150, "HydroSens"/M-ERA.NET Consortium
- 04/040/RGJ24/0278/Silesian University of Technology
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

