Real-Time Spectroscopic Ellipsometry for Flux Calibrations in Multi-Source Co-Evaporation of Thin Films: Application to Rate Variations in CuInSe2 Deposition
- PMID: 39203226
- PMCID: PMC11356208
- DOI: 10.3390/ma17164048
Real-Time Spectroscopic Ellipsometry for Flux Calibrations in Multi-Source Co-Evaporation of Thin Films: Application to Rate Variations in CuInSe2 Deposition
Abstract
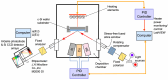
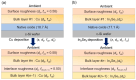
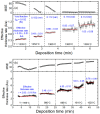
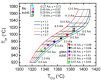
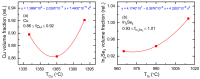
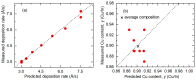
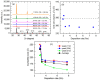
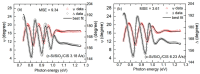
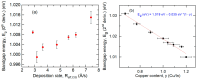
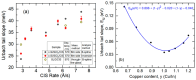
Flux calibrations in multi-source thermal co-evaporation of thin films have been developed based on real-time spectroscopic ellipsometry (RTSE) measurements. This methodology has been applied to fabricate CuInSe2 (CIS) thin film photovoltaic (PV) absorbers, as an illustrative example, and their properties as functions of deposition rate have been studied. In this example, multiple Cu layers are deposited step-wise onto the same Si wafer substrate at different Cu evaporation source temperatures (TCu). Multiple In2Se3 layers are deposited similarly at different In source temperatures (TIn). Using RTSE, the Cu and In2Se3 deposition rates are determined as functions of TCu and TIn. These rates, denoted Reff, are measured in terms of effective thickness which is the volume per planar substrate area and accounts for surface roughness variations with deposition time. By assuming that all incident metal atoms are incorporated into the films and that the atomic concentrations in the deposited material components are the same as in single crystals, initial estimates of the Cu and In atom fluxes can be made versus TCu and TIn. Applying these estimates to the co-evaporation of a set of CIS films from individual Cu, In, and Se sources, atomic concentration corrections can be assigned to the Cu and In2Se3 calibration films. The corrections enable generation of a novel calibration diagram predicting the atomic ratio y = [Cu]/[In] and rate Reff within the TCu-TIn plane. Using this diagram, optimization of the CIS properties as a PV absorber can be achieved versus both y and Reff.
Keywords: film composition; film deposition rate; film thickness; multi-source co-evaporation; real-time spectroscopic ellipsometry; thin film deposition; thin film deposition calibration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Vossen J.L., Kern W., editors. Thin Film Processes II. Academic; San Diego, CA, USA: 1991.
-
- Smith D.L. Thin-Film Deposition: Principles and Practice. McGraw Hill; New York, NY, USA: 1995.
-
- Mattox D.M. Handbook of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) Processing. William Andrew; Norwich, NY, USA: 1998.
-
- Messier R., Troiler-McKinstry S. Thin-film processes. In: Buschow K.H.J., Cahn R.W., Flemings M.C., Ilschner B., Kramer E.J., Mahajan S., Veyssière P., editors. Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology. 2nd ed. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2001. pp. 9307–9313.
-
- Thornton J.A. High rate thick film growth. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1977;7:239–260. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ms.07.080177.001323. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

