Pre- to Postbiotics: The Beneficial Roles of Pediatric Dysbiosis Associated with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
- PMID: 39203424
- PMCID: PMC11356122
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms12081582
Pre- to Postbiotics: The Beneficial Roles of Pediatric Dysbiosis Associated with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Abstract
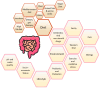
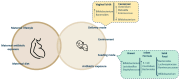
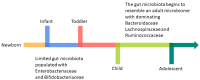
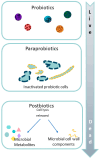
Probiotics are "live microorganisms which, when administered in adequate amount, confer health benefits on the host". They can be found in certain foods like yogurt and kefir and in dietary supplements. The introduction of bacterial derivatives has not only contributed to disease control but has also exhibited promising outcomes, such as improved survival rates, immune enhancement, and growth promotion effects. It is interesting to note that the efficacy of probiotics goes beyond the viability of the bacteria, giving rise to concepts like paraprobiotics, non-viable forms of probiotics, and postbiotics. Paraprobiotics offer various health benefits in children with intestinal dysbiosis, contributing to improved digestive health, immune function, and overall well-being. In this review, the potential of these therapeutic applications as alternatives to pharmacological agents for treating pediatric intestinal dysbiosis will be thoroughly evaluated. This includes an analysis of their efficacy, safety, long-term benefits, and their ability to restore gut microbiota balance, improve digestive health, enhance immune function, and reduce inflammation. The aim is to determine if these non-pharmacological interventions can effectively and safely manage intestinal dysbiosis in children, reducing the need for conventional medications and their side effects.
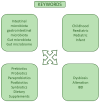
Keywords: dysbiosis; gut microbiota; infant; paraprobiotics; postbiotic; prebiotics; probiotics; synbiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prebiotics, Probiotics, Synbiotics, Paraprobiotics and Postbiotic Compounds in IBD.Biomolecules. 2021 Dec 18;11(12):1903. doi: 10.3390/biom11121903. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34944546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential of paraprobiotics and postbiotics to modulate the immune system: A Review.Microbiol Res. 2023 Oct;275:127449. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2023.127449. Epub 2023 Jul 6. Microbiol Res. 2023. PMID: 37454427 Review.
-
Role of Postbiotics in Diet-Induced Metabolic Disorders.Nutrients. 2022 Sep 7;14(18):3701. doi: 10.3390/nu14183701. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36145077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How to Improve Health with Biological Agents-Narrative Review.Nutrients. 2022 Apr 20;14(9):1700. doi: 10.3390/nu14091700. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35565671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Postbiotics and paraprobiotics: From concepts to applications.Food Res Int. 2020 Oct;136:109502. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109502. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Food Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32846581 Review.
Cited by
-
Postbiotics and Parabiotics: A Viable Health Promoting Alternative for Poultry Industry-A Comprehensive Review.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025 Aug 13. doi: 10.1007/s12602-025-10708-x. Online ahead of print. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025. PMID: 40802224 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

