Genomic Characterization of Bacillus pumilus Sonora, a Strain with Inhibitory Activity against Vibrio parahaemolyticus-AHPND and Probiotic Candidate for Shrimp Aquaculture
- PMID: 39203465
- PMCID: PMC11356620
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms12081623
Genomic Characterization of Bacillus pumilus Sonora, a Strain with Inhibitory Activity against Vibrio parahaemolyticus-AHPND and Probiotic Candidate for Shrimp Aquaculture
Abstract
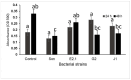
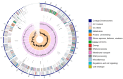
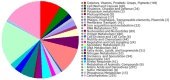
Acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease, caused by Vibrio parahaemolyticus strains carrying the pirA and pirB toxin genes (VpAHPND), has been causing great economic losses in Asia and America in the shrimp farming industry. Numerous strains are resistant to antibiotics. However, supplementation with probiotic antagonists has become a more desirable treatment alternative. Fourteen strains of microorganisms were assessed for their potential to inhibit VpAHPND in vitro activity. The bacteria with the highest activity were challenged with VpAHPND-infected Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Furthermore, the genomic characteristics of probiotic bacteria were explored by whole-genome sequencing. We identified the Sonora strain as Bacillus pumilus, which possesses positive proteolytic and cellulolytic activities that may improve shrimp nutrient uptake and digestion. Challenge trials showed a low cumulative mortality (11.1%). B. pumilus Son has a genome of 3,512,470 bp and 3734 coding sequences contained in 327 subsystems. Some of these genes are related to the biosynthesis of antimicrobial peptides (surfactins, fengycin, schizokinen, bacilibactin, and bacilysin), nitrogen and phosphorus metabolism, and stress response. Our in vitro and in vivo findings suggest that B. pumilus Sonora has potential as a functional probiotic.
Keywords: Bacillus pumilus; Sonora strain; Vibrio parahaemolyticus-AHPND; antimicrobial peptides (AMP); probiotic; whole genome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Stieglitz J.D., Touchton M., Benetti D.D., Rothen D., Clark-Hughes A., Haus B.K., Zangroniz A., Suman D.O. Chapter 5: Global Marine Aquaculture Development. In: Spalding A., Suman D., editors. Ocean and Society an Introduction to Marine Studies. Routledge; London, UK: 2023. pp. 59–78. - DOI
-
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations . The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture Blue Transformation in Action. FAO; Rome, Italy: 2024. 264p. - DOI
-
- [CONAPESCA] Comisión Nacional de Acuacultura y Pesca Anuario Estadístico de Acuacultura y Pesca. CONAPESCA, México. 2021. [(accessed on 14 June 2024)]. Available online: https://nube.conapesca.gob.mx/sites/cona/dgppe/2021/ANUARIO_ESTADISTICO_....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

