The Role of Akkermansia muciniphila on Improving Gut and Metabolic Health Modulation: A Meta-Analysis of Preclinical Mouse Model Studies
- PMID: 39203469
- PMCID: PMC11356609
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms12081627
The Role of Akkermansia muciniphila on Improving Gut and Metabolic Health Modulation: A Meta-Analysis of Preclinical Mouse Model Studies
Abstract
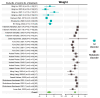
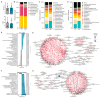
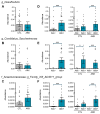
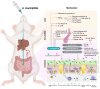
Akkermansia muciniphila (A. muciniphila) and its derivatives, including extracellular vesicles (EVs) and outer membrane proteins, are recognized for enhancing intestinal balance and metabolic health. However, the mechanisms of Akkermansia muciniphila's action and its effects on the microbiome are not well understood. In this study, we examined the influence of A. muciniphila and its derivatives on gastrointestinal (GI) and metabolic disorders through a meta-analysis of studies conducted on mouse models. A total of 39 eligible studies were identified through targeted searches on PubMed, Web of Science, Science Direct, and Embase until May 2024. A. muciniphila (alive or heat-killed) and its derivatives positively affected systemic and gut inflammation, liver enzyme level, glycemic response, and lipid profiles. The intervention increased the expression of tight-junction proteins in the gut, improving gut permeability in mouse models of GI and metabolic disorders. Regarding body weight, A. muciniphila and its derivatives prevented weight loss in animals with GI disorders while reducing body weight in mice with metabolic disorders. Sub-group analysis indicated that live bacteria had a more substantial effect on most analyzed biomarkers. Gut microbiome analysis using live A. muciniphila identified a co-occurrence cluster, including Desulfovibrio, Family XIII AD3011 group, and Candidatus Saccharimonas. Thus, enhancing the intestinal abundance of A. muciniphila and its gut microbial clusters may provide more robust health benefits for cardiometabolic, and age-related diseases compared with A. muciniphila alone. The mechanistic insight elucidated here will pave the way for further exploration and potential translational applications in human health.
Keywords: Akkermansia muciniphila; Candidatus Saccharimonas; Desulfovibrio; Family XIII AD3011 group; gut; inflammation; metabolic health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
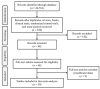
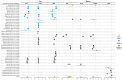
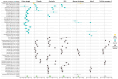
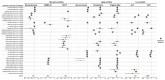
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

